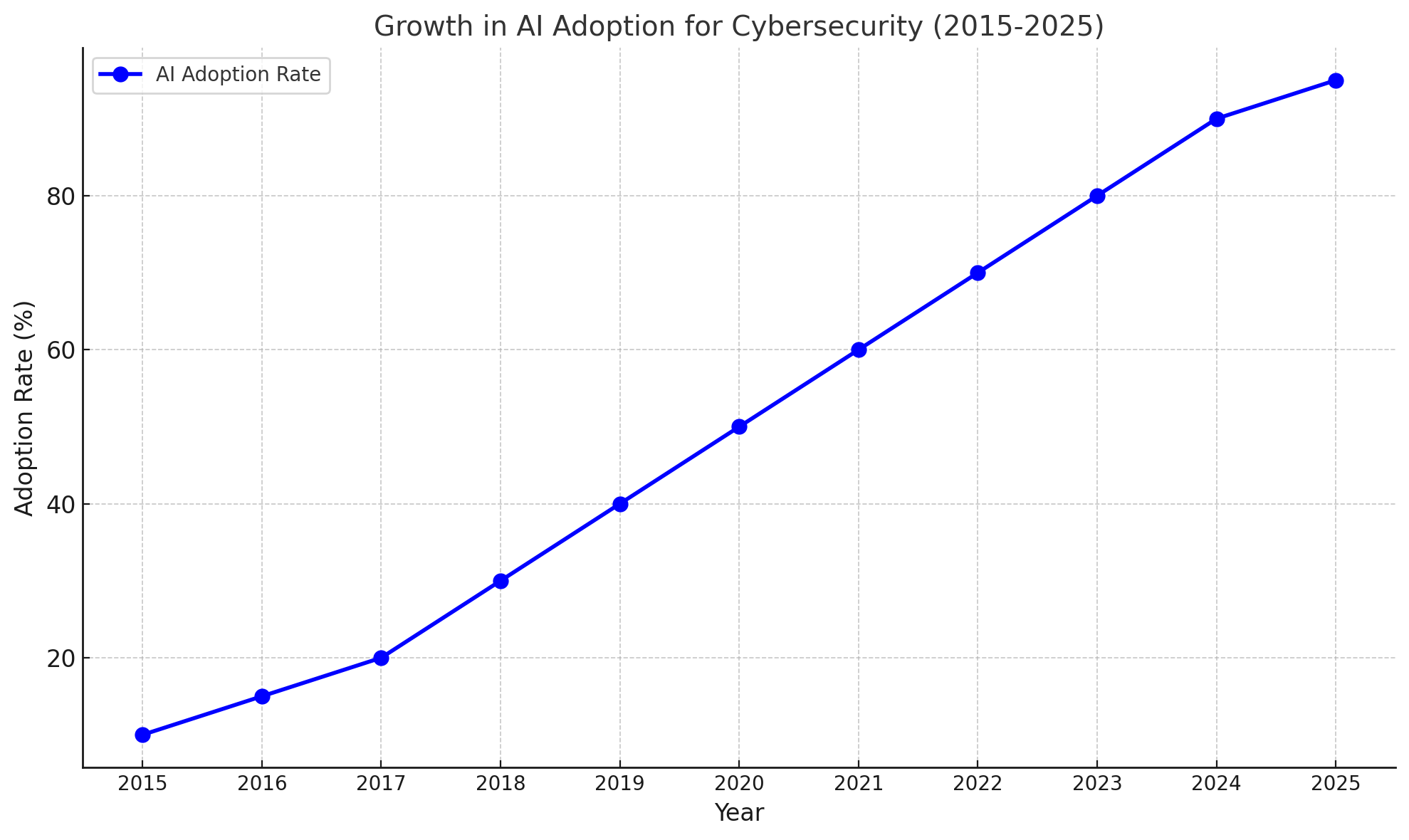
As the digital landscape evolves, so does the complexity and scale of cyber threats. Traditional cybersecurity measures, while effective to an extent, often struggle to keep pace with increasingly sophisticated attacks. Enter Artificial Intelligence (AI), a game-changer that is redefining how organizations approach threat detection and defense. From real-time anomaly detection to predictive analytics, AI is revolutionizing cybersecurity, offering unparalleled precision and speed.
This blog explores the intersection of AI and cybersecurity, detailing its benefits, challenges, applications, and the transformative role it plays in safeguarding the digital realm. Accompanied by charts, graphs, and infographics, this comprehensive guide delves into the future of AI-powered cybersecurity.
The Evolution of Cyber Threats
The Growing Complexity of Cyber Attacks
Cybercriminals are leveraging advanced tools and techniques to bypass traditional defenses. Common threats include:
- Phishing Attacks: Sophisticated schemes targeting individuals and organizations.
- Ransomware: Malicious software encrypting data and demanding payment for its release.
- Zero-Day Exploits: Attacks exploiting unpatched software vulnerabilities.
- Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS): Overwhelming systems to cause disruptions.
The Limitations of Traditional Cybersecurity
Traditional systems rely on predefined rules and signatures, which often fail to detect novel or evolving threats. Manual threat analysis is time-consuming and resource-intensive, leaving organizations vulnerable.
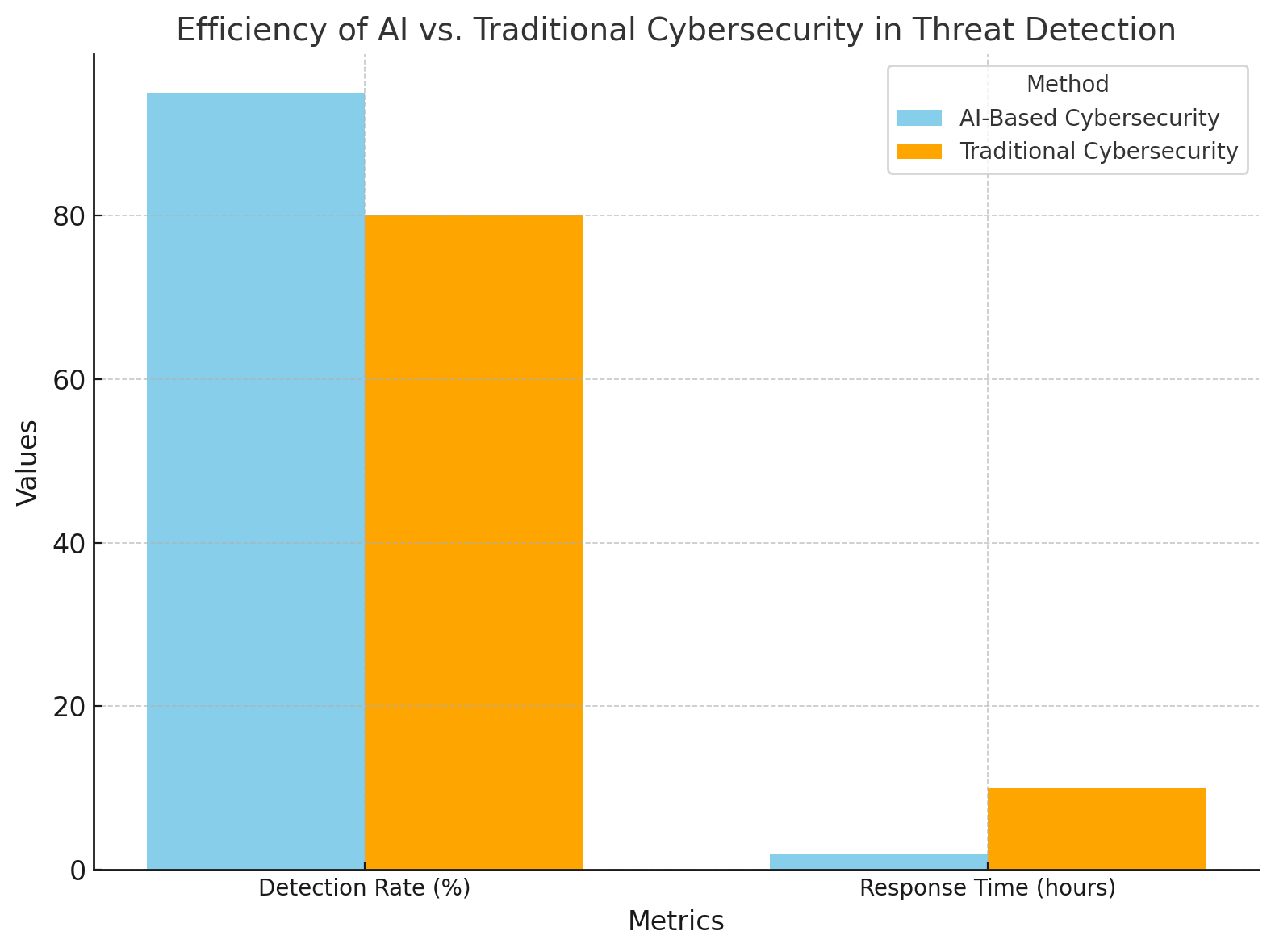
How AI Enhances Cybersecurity
1. Real-Time Threat Detection
AI systems analyze vast amounts of data in real-time, identifying anomalies and flagging potential threats.
2. Predictive Analytics
Machine learning models predict future threats by analyzing historical data and identifying patterns.
3. Automated Incident Response
AI can automatically neutralize threats, such as isolating infected systems or blocking malicious traffic.
4. Advanced Malware Analysis
AI-powered tools dissect malware, understanding its behavior and preventing future attacks.
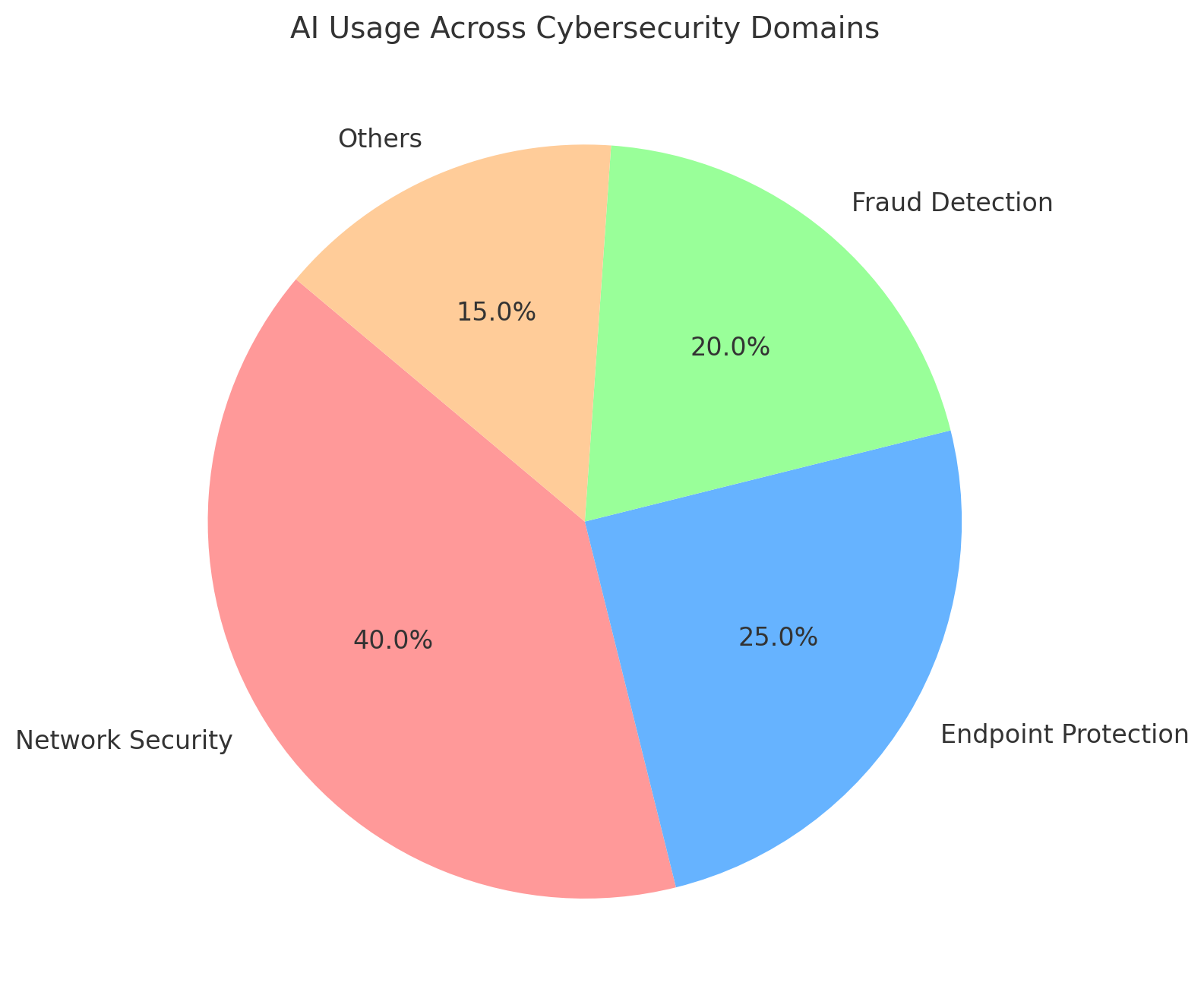
Applications of AI in Cybersecurity
1. Network Security
- AI monitors network traffic to detect unusual activity.
- Real-time alerts for potential breaches.
2. Endpoint Protection
- AI secures devices like laptops, smartphones, and IoT devices from attacks.
- Predictive models identify and mitigate vulnerabilities.
3. Fraud Detection
- AI systems analyze transactions to detect anomalies and prevent fraudulent activities.
4. Email Security
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) identifies phishing attempts and malicious content.
Benefits of AI-Powered Cybersecurity
1. Proactive Defense
AI anticipates threats before they materialize, allowing organizations to stay ahead.
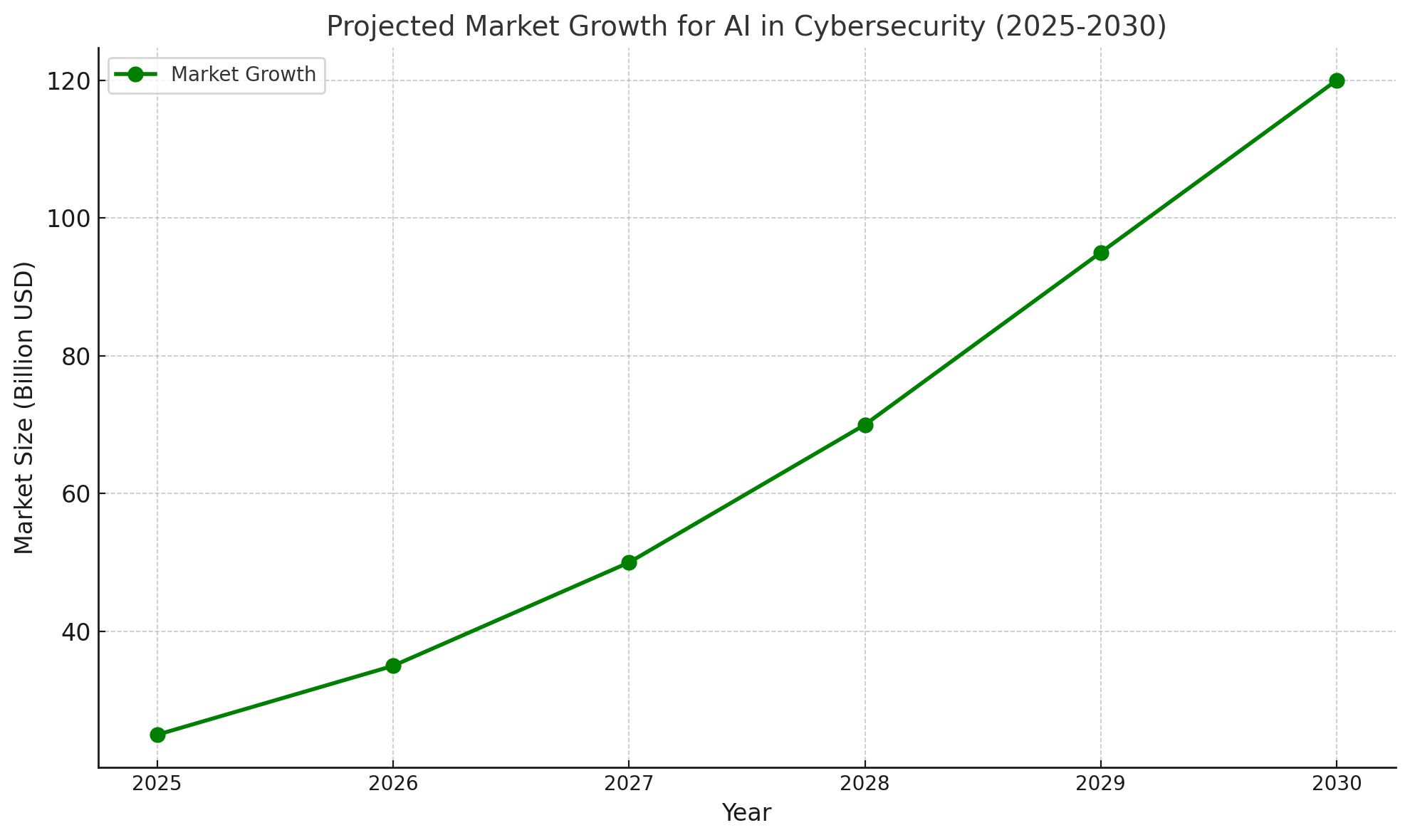
2. Scalability
AI solutions adapt to handle growing amounts of data and increasingly complex threats.
3. Reduced Human Error
By automating repetitive tasks, AI minimizes the risk of oversight and errors.
4. Enhanced Accuracy
Machine learning models continually improve, providing precise threat detection.
Challenges of AI in Cybersecurity
1. False Positives
AI systems may incorrectly flag benign activities, leading to resource drain.
2. Adversarial Attacks
Cybercriminals use AI to identify and exploit weaknesses in security systems.
3. Data Dependency
AI relies on high-quality data; biased or incomplete datasets can compromise effectiveness.
4. Cost and Complexity
Implementing AI systems requires significant investment and expertise.
Case Studies: AI in Action
1. Financial Services
- AI prevents fraud by analyzing transaction patterns and detecting anomalies.
- Example: JPMorgan Chase’s AI-driven fraud detection systems.
2. Healthcare
- AI secures patient records and prevents ransomware attacks.
- Example: AI tools flagging unusual access to medical data.
3. Government and Defense
- AI enhances national security by detecting and neutralizing cyber threats.
- Example: AI-driven systems monitoring critical infrastructure.
Future Trends in AI-Powered Cybersecurity
1. AI-Augmented Threat Intelligence
Advanced AI models will provide deeper insights into emerging threats.
2. Behavioral Biometrics
AI will leverage behavioral patterns for enhanced user authentication.
3. Integration with Quantum Computing
AI and quantum computing will collaborate to tackle complex cybersecurity challenges.
4. AI for Insider Threat Detection
Sophisticated algorithms will identify malicious actions by trusted individuals.
Best Practices for Implementing AI in Cybersecurity
1. Start with a Pilot Program
Test AI solutions in a controlled environment before full-scale implementation.
2. Ensure Data Quality
Use clean and unbiased datasets to train AI models.
3. Collaborate Across Teams
Involve IT, security, and operational teams in AI adoption.
4. Regular Audits
Periodically review AI systems to ensure optimal performance and compliance.
Conclusion
AI is revolutionizing cybersecurity, offering powerful tools to detect and defend against modern threats. While challenges remain, the benefits of AI-powered solutions far outweigh the drawbacks. By leveraging AI, organizations can enhance their security posture, protect sensitive data, and build trust in an increasingly digital world.
As cyber threats grow in sophistication, the integration of AI in cybersecurity is not just an option—it’s a necessity. The future belongs to those who embrace innovation and proactively safeguard their digital assets.
FAQs
AI-powered automation uses artificial intelligence to perform tasks traditionally done by humans, such as decision-making, data processing, and repetitive workflows. It is changing the future of work by increasing efficiency, reducing errors, and enabling employees to focus on creative, strategic, and higher-value tasks, thereby reshaping roles across industries.
Industries experiencing significant transformation include:
- Manufacturing: Through smart factories, robotics, and predictive maintenance.
- Healthcare: By streamlining diagnostics, administrative tasks, and personalized treatments.
- Retail: With automated inventory management, customer insights, and checkout processes.
- Finance: Through fraud detection, risk analysis, and automated financial planning.
- Transportation: Via autonomous vehicles and optimized logistics systems.
While AI-powered automation will replace some routine and repetitive jobs, it will create new opportunities in tech development, data analysis, and AI system management. The shift emphasizes the need for upskilling and reskilling workers to adapt to emerging roles and technologies.
Key challenges include high implementation costs, integration with existing systems, managing workforce transitions, and addressing ethical concerns like data privacy and algorithmic bias. Businesses must develop strategies for smooth adoption, workforce retraining, and maintaining transparency in AI-driven processes.





