Automation has always been a driving force behind industrial revolutions, but artificial intelligence (AI) is taking it to unprecedented heights. From streamlining operations to enhancing decision-making, AI-powered automation is poised to transform the workforce and redefine industries. This blog delves into the evolving landscape of AI-driven automation, exploring its applications, benefits, challenges, and the future of work in an increasingly automated world. We’ll also incorporate visual aids like charts, graphs, and infographics to provide a comprehensive understanding of this transformative trend.
Understanding AI-Powered Automation
What is AI-Powered Automation?
AI-powered automation combines machine learning, natural language processing (NLP), and robotics to execute tasks with minimal human intervention. Unlike traditional automation, which relies on predefined rules, AI systems learn and adapt over time, making them more flexible and efficient.
How is it Different from Traditional Automation?
- Learning Capability: AI systems continuously learn and improve from data.
- Complex Problem-Solving: AI can handle unstructured data and make decisions.
- Scalability: AI-driven systems adapt to changing demands seamlessly.
Key Applications of AI-Powered Automation
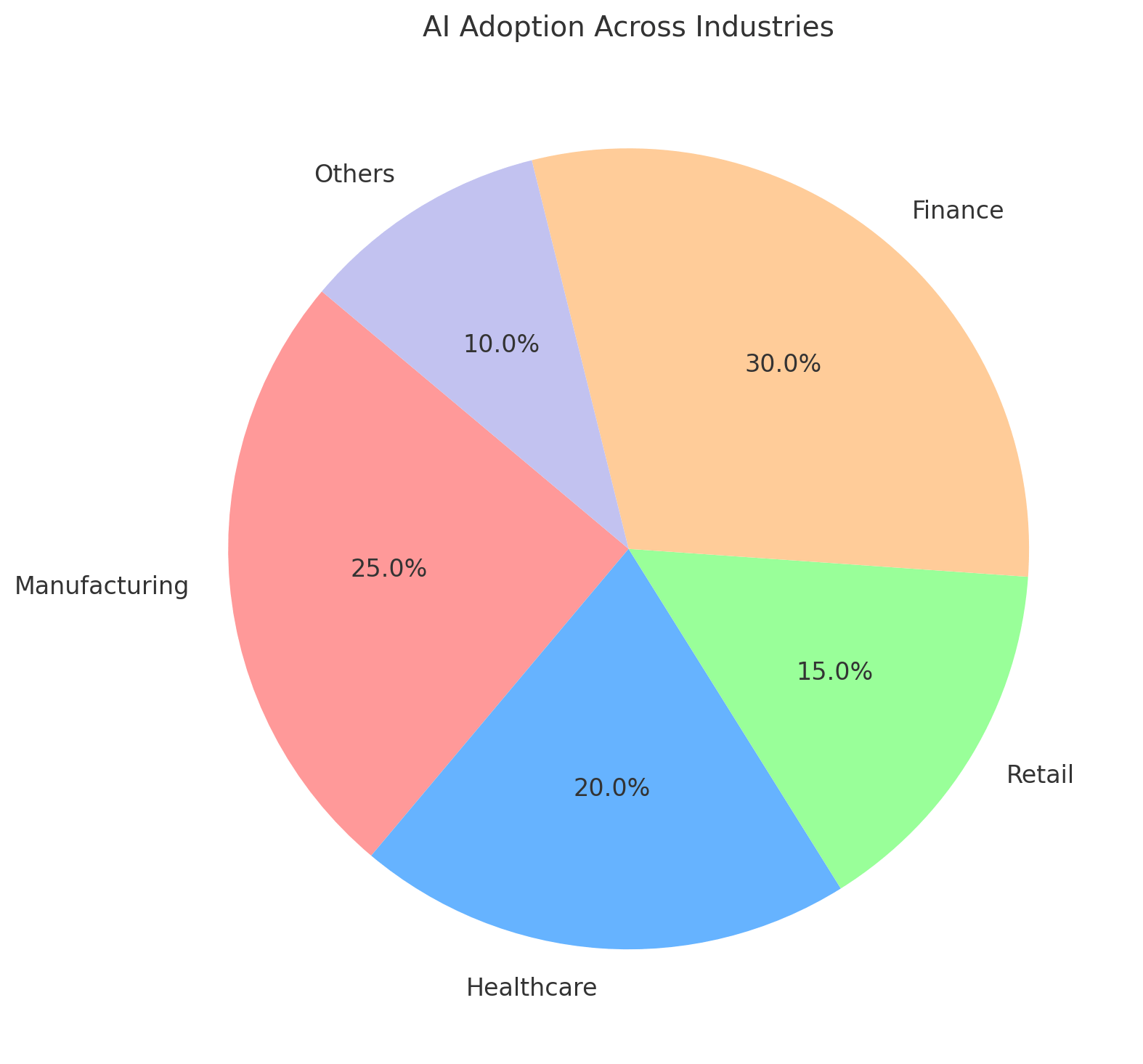
1. Manufacturing and Supply Chain
- Smart Factories: AI optimizes production schedules, reduces downtime, and improves quality control.
- Predictive Maintenance: AI-powered systems predict equipment failures, minimizing disruptions.
- Logistics: Automation in inventory management and delivery routing.
2. Healthcare
- Diagnostics: AI analyzes medical images and data for accurate diagnoses.
- Robotic Surgery: Precision-driven procedures with minimal invasiveness.
- Patient Management: Automated systems for scheduling and follow-ups.
3. Retail and E-Commerce
- Personalized Shopping Experiences: AI-driven recommendation engines.
- Inventory Management: Real-time stock updates and demand forecasting.
- Automated Customer Support: Chatbots and virtual assistants.
4. Financial Services
- Fraud Detection: AI identifies suspicious activities in real-time.
- Algorithmic Trading: Automated trading decisions based on market data.
- Customer Insights: Personalized financial advice through data analysis.
Benefits of AI-Powered Automation
1. Increased Productivity
AI reduces repetitive tasks, enabling employees to focus on high-value activities.
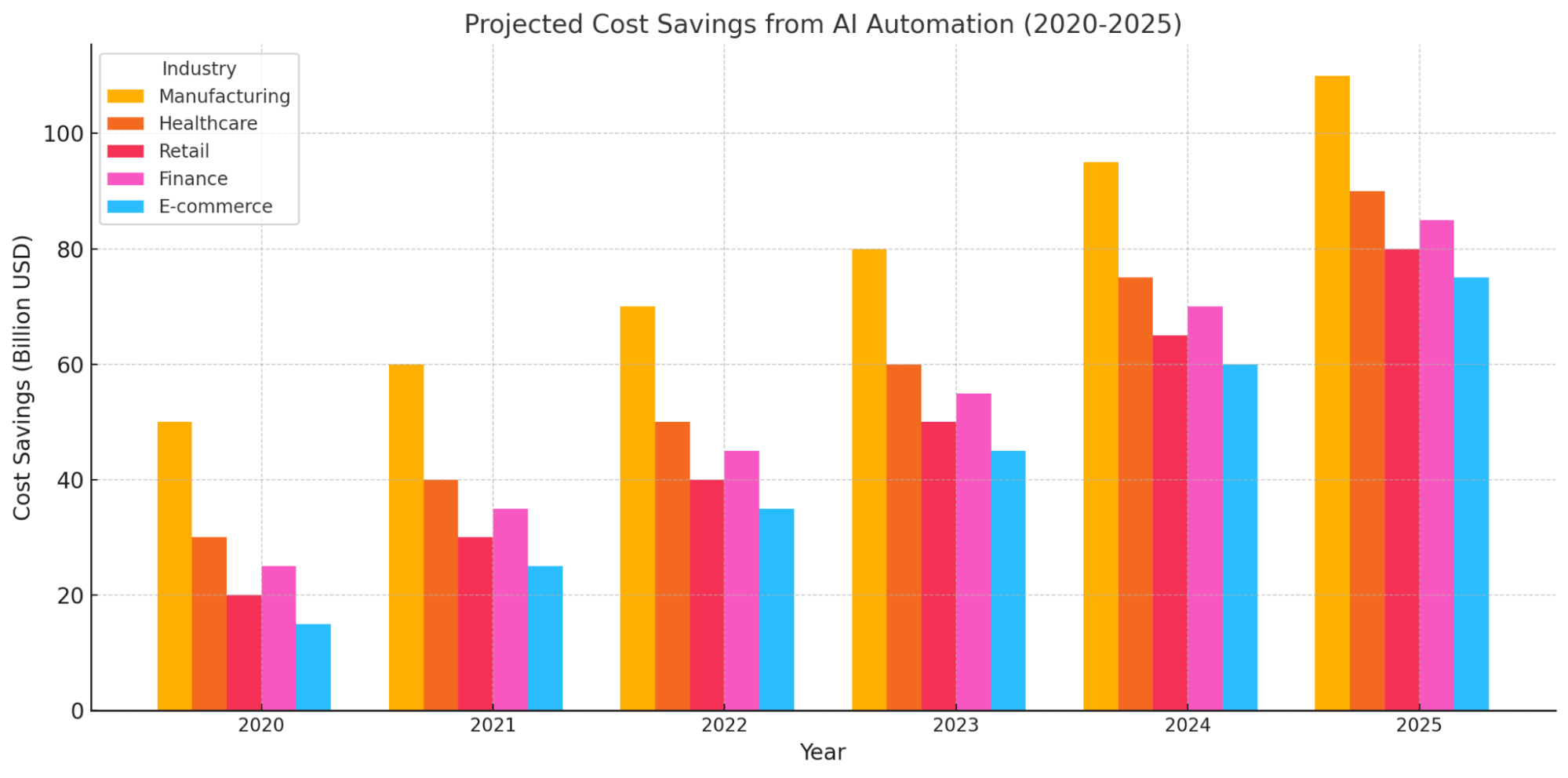
2. Cost Savings
Automation minimizes operational costs by improving efficiency and reducing errors
3. Enhanced Decision-Making
AI provides actionable insights through data analysis.
4. Scalability
AI systems can adapt to growing demands without significant resource investments
Challenges of AI-Powered Automation
1. Workforce Displacement
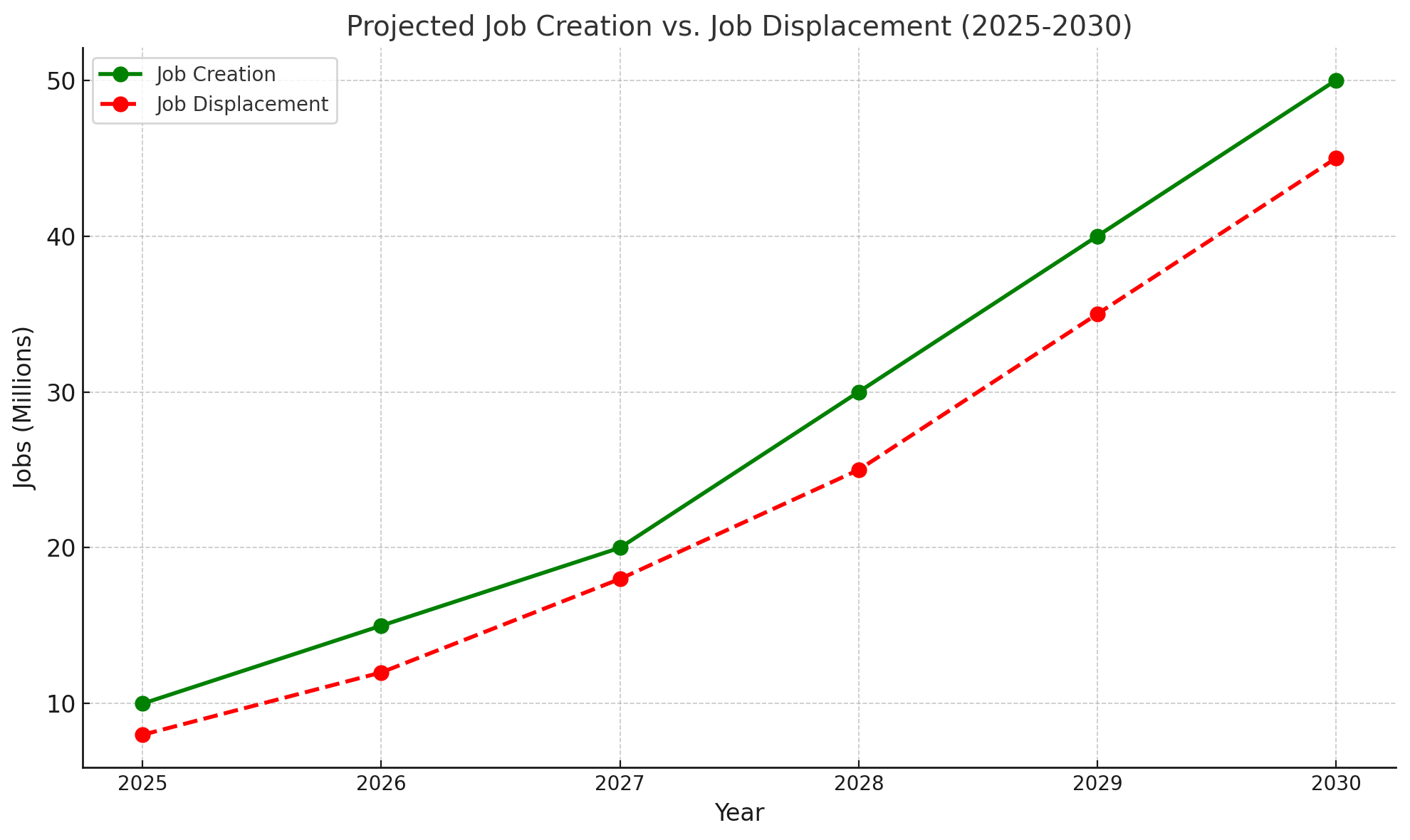
- Transitioning to an automated workforce may lead to job losses in certain sectors.
- Upskilling and reskilling programs are essential to mitigate this impact.
2. Ethical Concerns
- Bias in AI algorithms.
- Transparency in decision-making processes.
3. Data Security and Privacy
- Ensuring robust cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive data.
The Future of Work: A Hybrid Model
1. Collaboration Between Humans and Machines
AI will complement human capabilities, handling routine tasks while humans focus on creativity and strategic decision-making.
2. Reskilling the Workforce
Continuous learning programs will be crucial to prepare employees for AI-driven roles.
3. New Job Opportunities
AI will create demand for roles in AI development, maintenance, and oversight.
Industry-Specific Impacts of AI Automation
1. Manufacturing
- Fully automated production lines.
- Real-time supply chain management.
2. Healthcare
- AI-driven drug discovery and telemedicine.
- Enhanced patient care through predictive analytics.
3. Retail
- Autonomous stores with cashier-less checkouts.
- Hyper-personalized marketing campaigns.
4. Finance
- Instant loan approvals through AI.
- Enhanced risk management using predictive models.
Case Studies
1. Tesla’s Automated Manufacturing
Tesla’s gigafactories showcase the potential of AI-powered automation in streamlining production processes.
2. Amazon’s Warehousing
Amazon’s use of robots and AI in warehousing has revolutionized inventory management and order fulfillment.
3. IBM Watson in Healthcare
IBM Watson leverages AI to assist doctors in diagnosing diseases and developing treatment plans.
Best Practices for Implementing AI Automation
1. Start Small
Begin with pilot projects to test feasibility and scalability.
2. Invest in Training
Equip employees with skills to work alongside AI systems
3. Focus on Data Quality
Ensure high-quality data for accurate AI predictions and decisions.
4. Monitor and Optimize
Continuously evaluate AI systems to enhance performance and address challenges.
Conclusion
AI-powered automation is reshaping industries and redefining the future of work. While it offers unparalleled benefits in efficiency, cost savings, and innovation, it also brings challenges that require careful consideration. By embracing a hybrid workforce model, investing in reskilling, and adopting ethical AI practices, businesses can unlock the full potential of AI-driven automation.
As we move into an era of intelligent automation, organizations must adapt to stay competitive in a rapidly evolving landscape. The journey may be complex, but the rewards are immense for those who navigate it effectively.
FAQs
AI-powered automation involves using artificial intelligence to perform tasks traditionally handled by humans, such as data analysis, decision-making, and repetitive processes. It is transforming industries by improving efficiency, reducing costs, enhancing accuracy, and enabling the development of new business models. From manufacturing and logistics to healthcare and customer service, AI-driven tools are reshaping how businesses operate.
AI-powered automation is impacting a wide range of industries, including:
- Manufacturing: Through robotics and smart factories.
- Healthcare: By improving diagnostics, streamlining administrative tasks, and enabling personalized treatments.
- Retail: Through inventory management, customer personalization, and automated checkouts.
- Finance: By automating fraud detection, underwriting, and financial advising.
- Transportation: With autonomous vehicles and optimized logistics.
AI-powered automation will likely displace some jobs that involve repetitive or routine tasks while creating new roles that require advanced technical, analytical, and creative skills. It will also lead to a greater emphasis on upskilling and reskilling the workforce to adapt to emerging technologies, fostering a shift toward more specialized and strategic positions.
Businesses can prepare by investing in AI technologies that align with their strategic goals, fostering a culture of innovation, and prioritizing workforce development through training programs. Emphasizing ethical AI practices, ensuring transparent decision-making, and balancing automation with human expertise will also be critical to successfully navigating this transformative shift.





