The shift to remote work has transformed how organizations operate, bringing flexibility and new opportunities for productivity. However, this transformation has also introduced significant cybersecurity challenges. Distributed teams operate across various networks and devices, increasing vulnerabilities and exposing organizations to cyberattacks.
This blog explores the cybersecurity landscape in the age of remote work, highlights emerging threats, and offers best practices for protecting distributed teams. Charts, graphs, and visual aids provide actionable insights for businesses striving to secure their digital operations.
The Evolving Cybersecurity Landscape
The Rise of Remote Work
The global adoption of remote work accelerated in response to the COVID-19 pandemic. By 2025, approximately 70% of the workforce is expected to work remotely at least five days a month, according to recent industry reports.
New Cybersecurity Risks
Remote work environments have introduced:
- Insecure Home Networks: AEmployees rely on personal Wi-Fi setups that may lack robust security.
- Increased Phishing Attacks: Cybercriminals target employees with deceptive emails designed to steal credentials.
- Shadow IT: Unauthorized apps and tools used by remote teams can bypass official security measures.
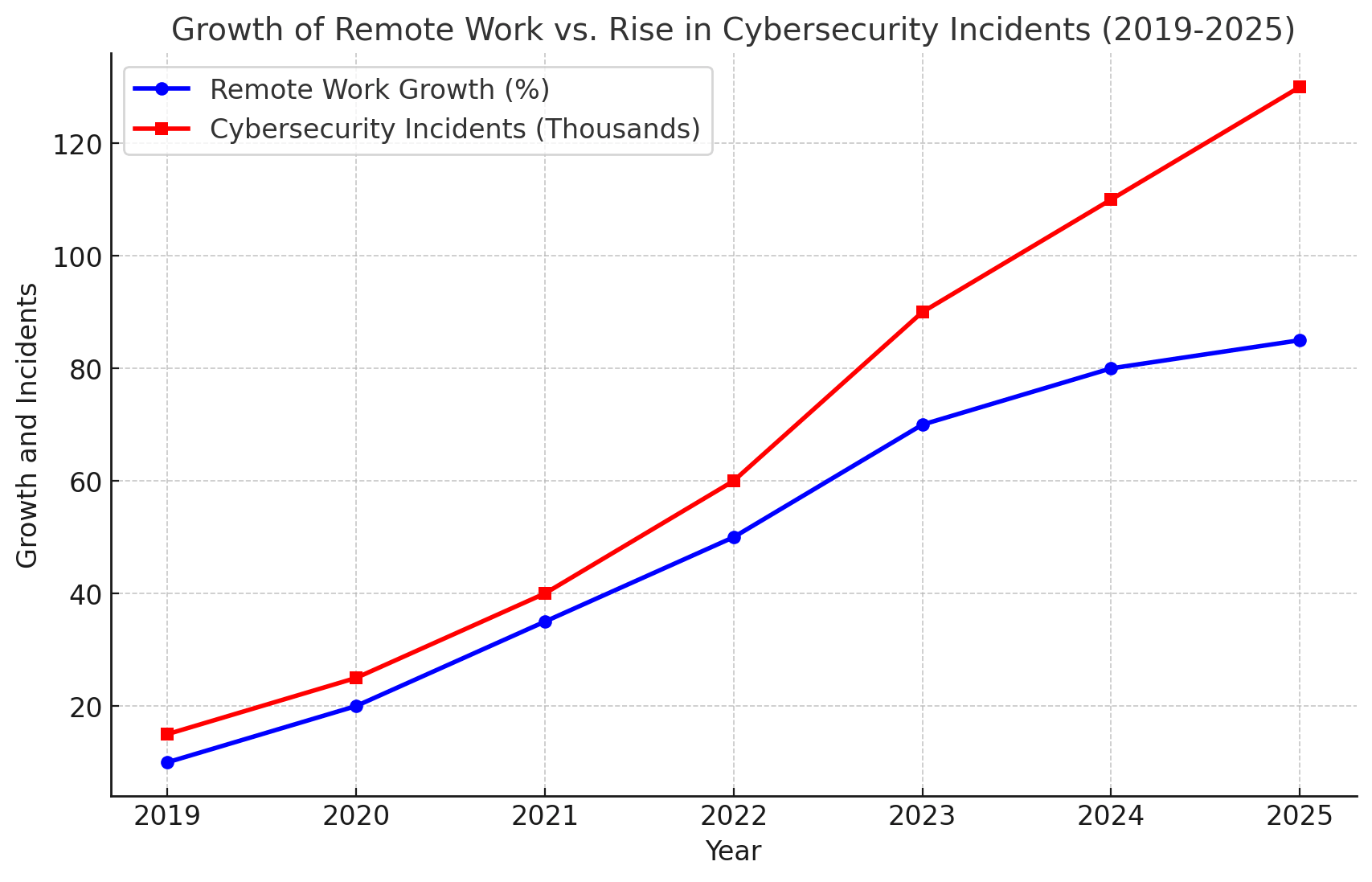
Top Cybersecurity Threats in Remote Work
1. Phishing and Social Engineering Attacks
Phishing remains one of the most common threats, with attackers impersonating trusted entities to steal sensitive information.
2. Ransomware
Ransomware attacks have surged as attackers exploit remote work vulnerabilities. In 2025, ransomware is expected to cause global damages exceeding $30 billion.
3. Insider Threats
Unintentional errors or malicious actions by employees can lead to significant data breaches.
4. Unsecured Endpoints
Remote devices are often more vulnerable to attacks due to inconsistent security configurations.
Best Practices for Securing Distributed Teams
1. Implement a Zero Trust Framework
Adopt a "never trust, always verify" approach by:
- Requiring multi-factor authentication (MFA).
- Verifying all users and devices before granting access.
- Continuously monitoring activities for anomalies.
2. Secure Endpoint Devices
- Enforce the use of company-provided devices with pre-installed security measures.
- Regularly update and patch software to mitigate vulnerabilities.
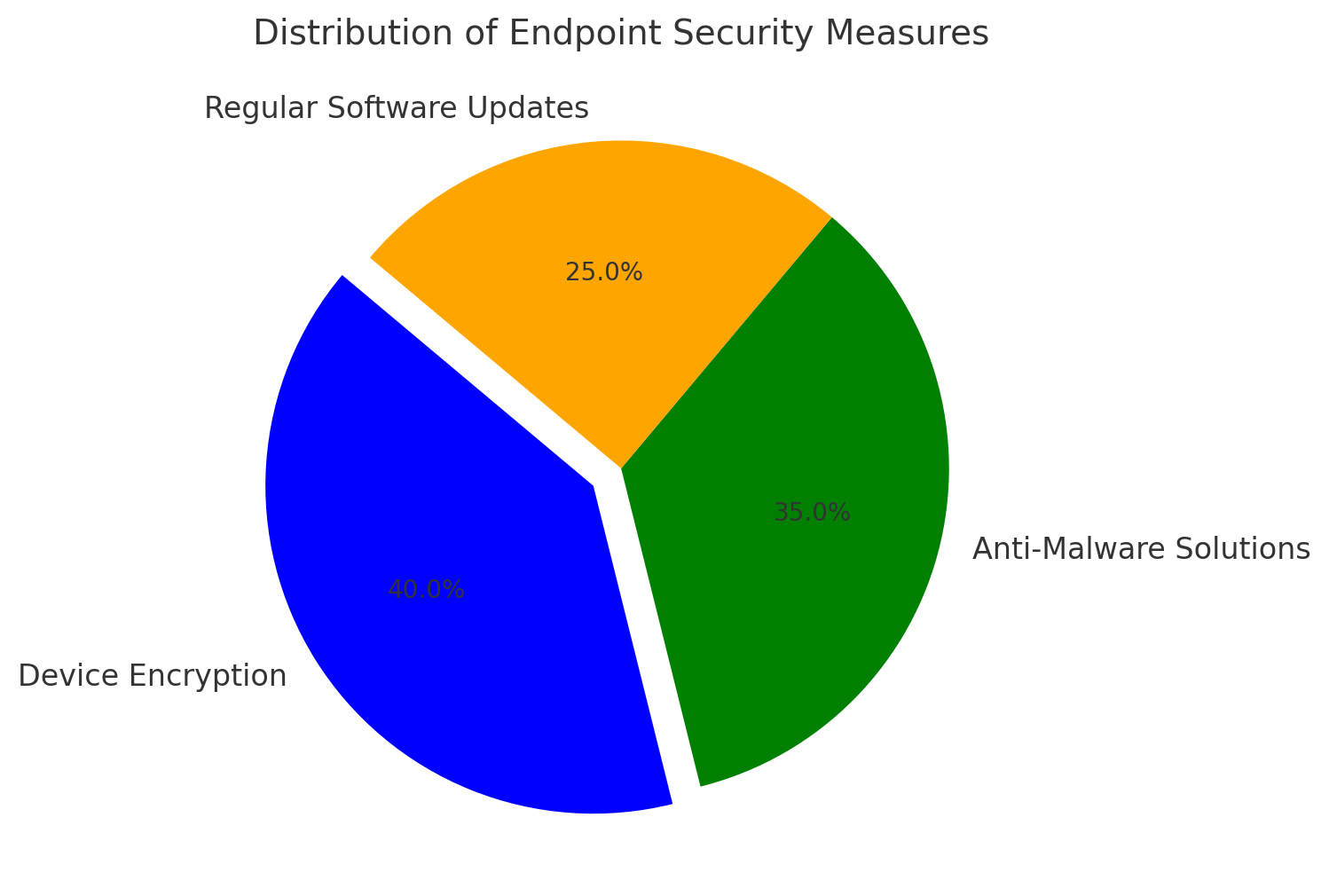
3. Strengthen Network Security
- Encourage employees to use virtual private networks (VPNs) for secure communication.
- Implement firewalls and intrusion detection systems.
4. Educate Employees on Cyber Hygiene
- Conduct regular training sessions on identifying phishing attempts.
- Create guidelines for password management and secure file sharing.
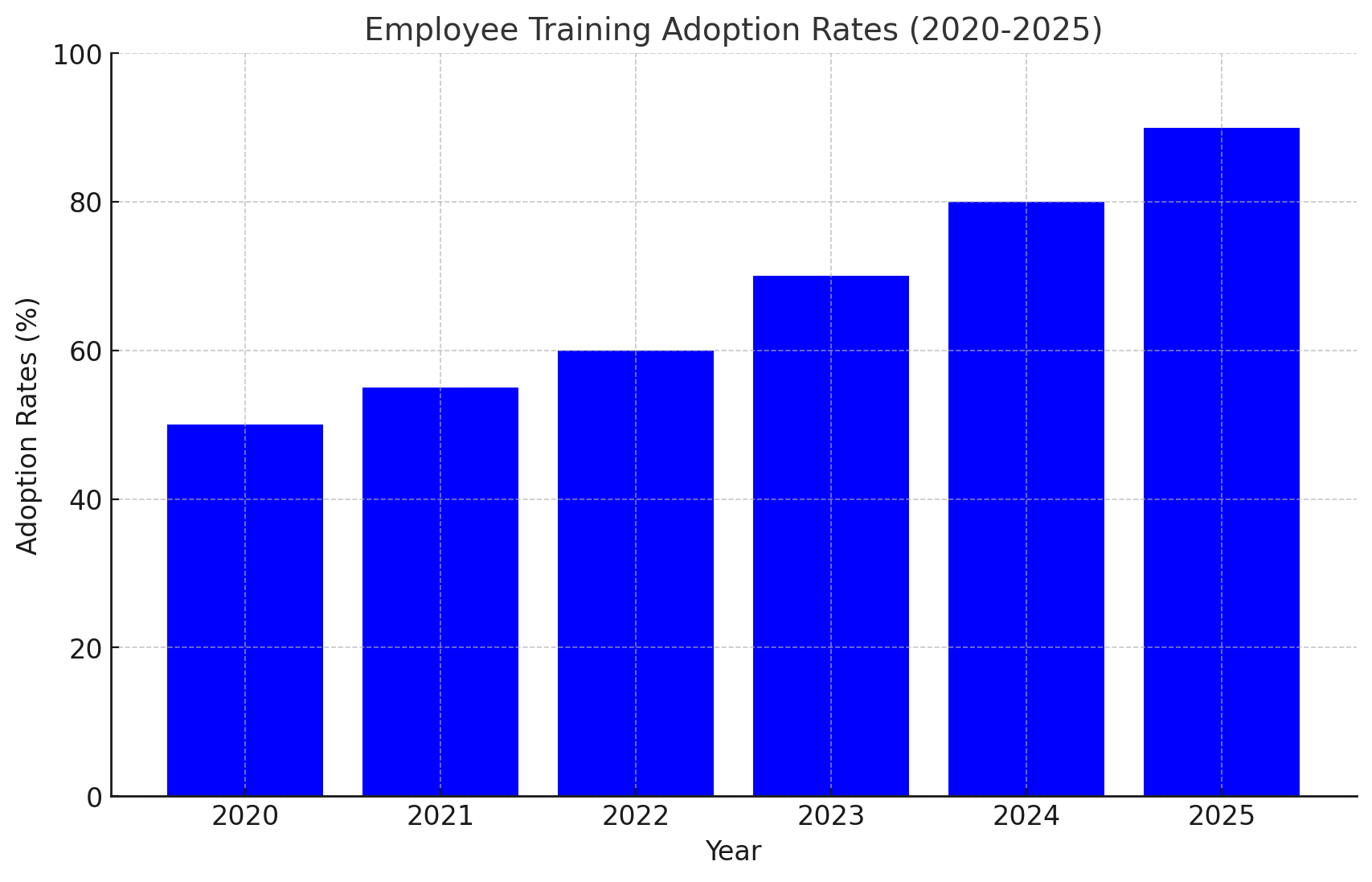
5. Develop a Remote Work Security Policy
Clearly define:
- Acceptable use of company devices and networks.
- Procedures for reporting suspicious activities.
- Role of Technology in Enhancing Cybersecurity.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning.
AI-powered tools can:
- Detect and respond to threats in real-time.
- Analyze vast amounts of data for anomalies.
Secure Collaboration Tools
Platforms like Microsoft Teams and Zoom have enhanced their security features to support remote teams, offering end-to-end encryption and administrative controls.
Cloud Security Solutions
Cloud providers offer robust security measures, including:
- Identity and access management (IAM).
- Data loss prevention (DLP) tools.
- Top Technologies Supporting Remote Work Security
Case Studies: Cybersecurity Success Stories
Case Study 1: A Tech Company Adopting Zero Trust
A leading tech firm transitioned to a Zero Trust model, significantly reducing unauthorized access attempts.
Case Study 2: Small Business Leveraging Cloud Security
A small business implemented cloud-based security tools, ensuring secure remote operations and regulatory compliance.
Metrics for Measuring Cybersecurity Success
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs):
- Phishing Simulation Success Rates: Percentage of employees avoiding simulated attacks.
- Incident Response Times: Speed of addressing security breaches.
- Patch Management Compliance: Percentage of devices updated within a given timeframe.
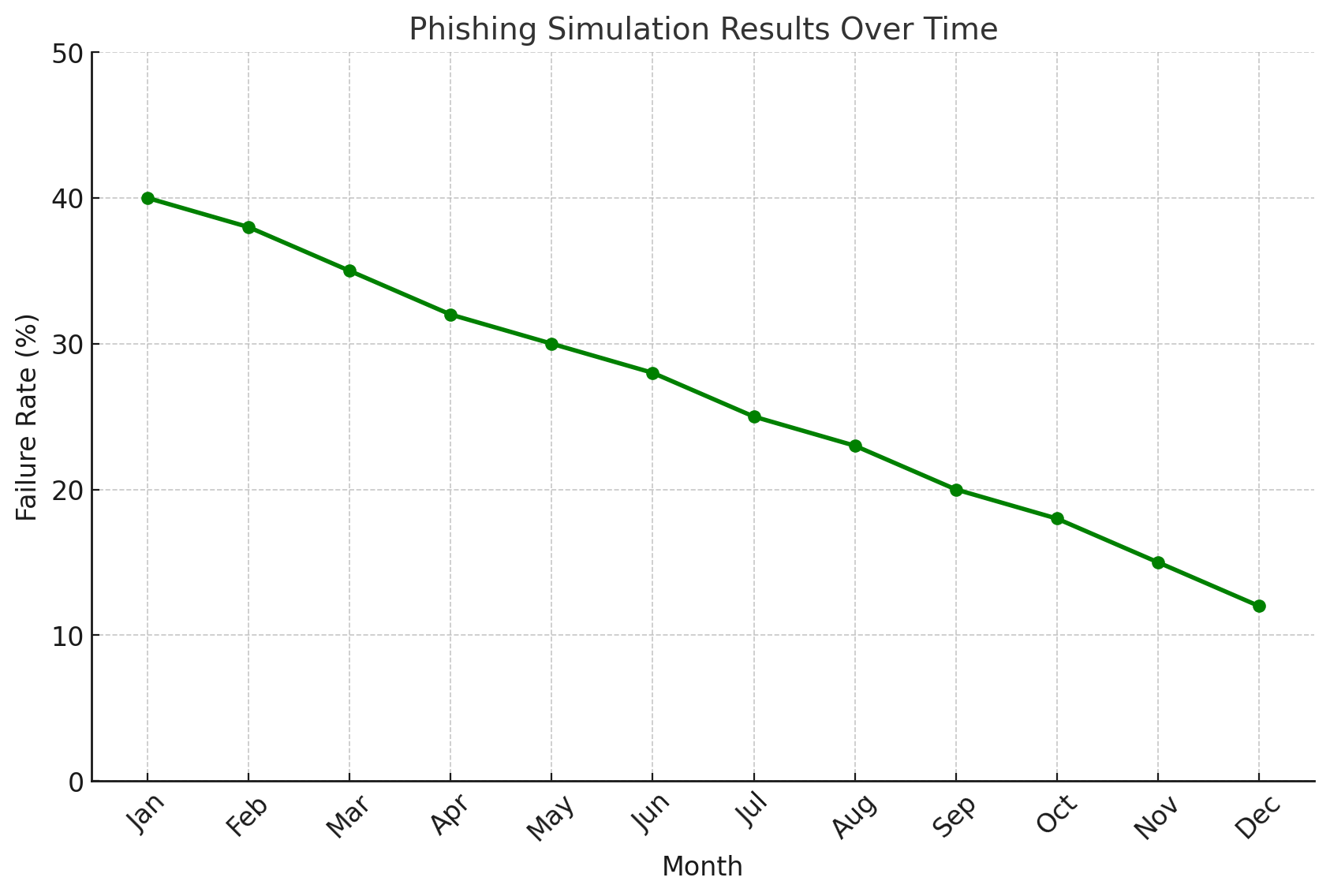
Future Trends in Cybersecurity for Remote Work
1. Increased Automation
Automation will play a larger role in identifying and responding to threats, reducing the burden on security teams.
2. Biometric Authentication
Advanced authentication methods like facial recognition and fingerprint scanning will enhance security.
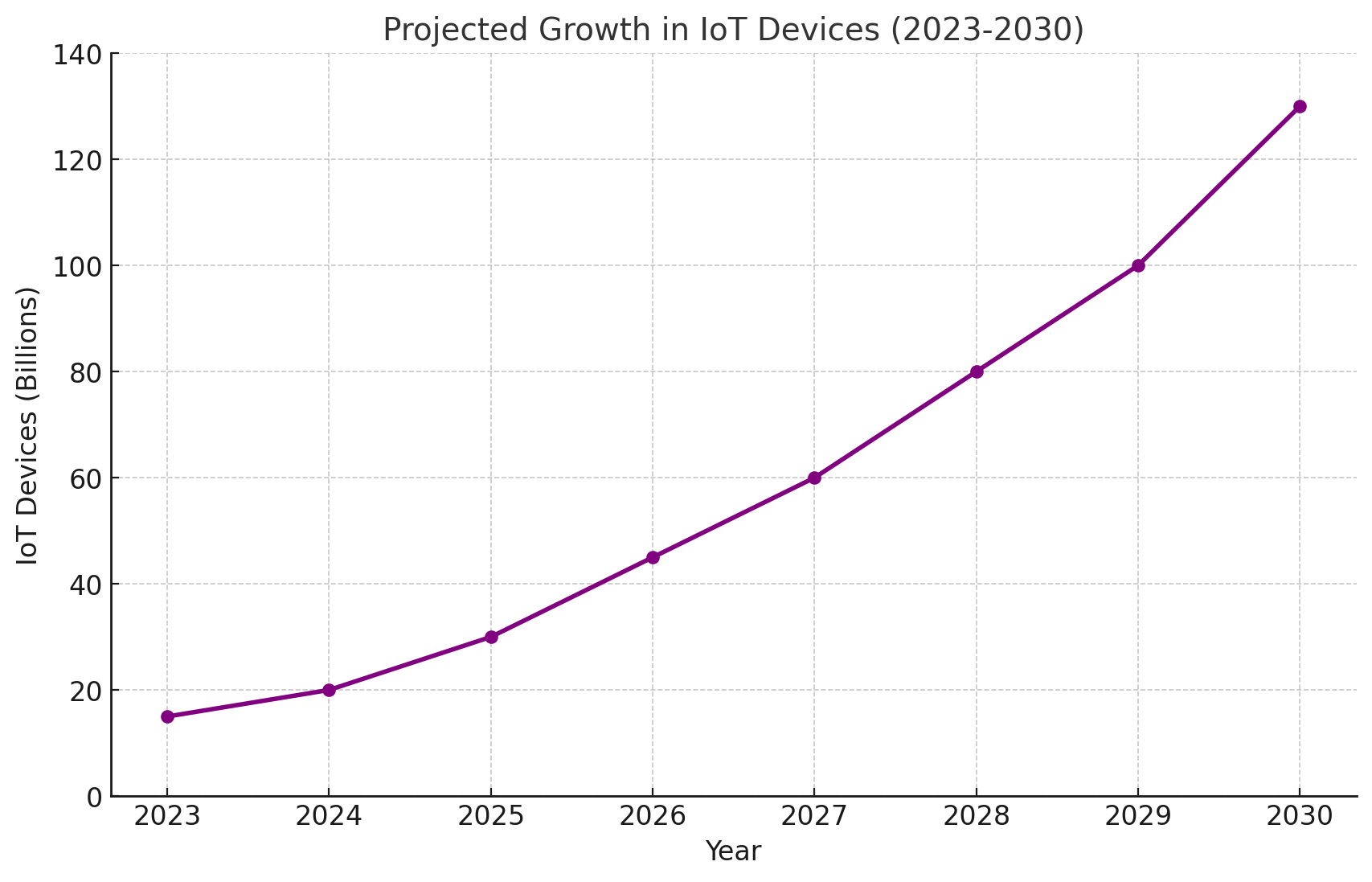
3. Integration of IoT Devices
As more IoT devices become part of remote work setups, securing them will be critical.
Conclusion
Cybersecurity in the age of remote work is a dynamic and evolving challenge. As distributed teams become the norm, organizations must adopt robust strategies to safeguard their operations. From implementing Zero Trust frameworks to leveraging AI-driven tools, there are numerous ways to enhance security.
By prioritizing cybersecurity and fostering a culture of awareness, businesses can protect their teams and thrive in an increasingly digital world. How is your organization addressing remote work cybersecurity? Share your strategies and insights below!
FAQs
Remote work introduces new challenges as employees access corporate networks from various locations and devices. Cyber threats like phishing, ransomware, and data breaches exploit these vulnerabilities. Ensuring strong cybersecurity practices protects sensitive company data, maintains compliance with regulations, and prevents financial and reputational damage.
- Use VPNs: Virtual Private Networks encrypt internet connections, securing data transmission.
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Adds an extra layer of protection beyond passwords.
- Update Software Regularly: Apply patches and updates to close security loopholes.
- Use Antivirus and Endpoint Security: Detects and prevents malicious activities.
- Secure Wi-Fi: Ensure home routers use strong encryption and passwords.
- Conduct Regular Training: Provide up-to-date knowledge on spotting phishing emails, social engineering, and suspicious links.
- Simulate Phishing Tests: Helps employees practice identifying malicious communications.
- Establish a Reporting Protocol: Encourage employees to report potential threats immediately.
- Develop Clear Policies: Ensure employees understand acceptable use and security protocols.
- Use Secure Tools: Opt for encrypted collaboration platforms like Slack, Microsoft Teams, or Zoom with secure settings enabled.
- Control Access Permissions: Restrict access to sensitive information to only those who need it.
- Implement Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Prevent unauthorized sharing or storage of sensitive data.
- Monitor for Unusual Activity: Use cybersecurity software to detect and respond to potential breaches in real-time.





