In today’s hyperconnected world, where remote work, cloud computing, and mobile technologies are the norm, traditional cybersecurity models are proving insufficient. The once-reliable perimeter-based security is now a liability, unable to protect against modern threats in a borderless digital ecosystem. Enter Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA), a revolutionary framework that eliminates the notion of trust within a network, enforcing strict verification for every user and device at every access point.
This blog explores the rise of Zero Trust Architecture, its principles, benefits, challenges, and why it is the future of cyber defense. We will also incorporate visual aids like charts, graphs, and infographics to provide a comprehensive understanding of this critical topic.
The Traditional Perimeter Model vs. Zero Trust
The Fall of Perimeter-Based Security
In the traditional cybersecurity model, organizations relied on a secure perimeter to guard their internal networks. Firewalls and VPNs were the primary defense mechanisms. However, this model struggles to address modern challenges such as:
- Remote Work: Employees accessing sensitive systems from outside the office network.
- Cloud Adoption: Expanding attack surfaces beyond on-premises systems.
- Sophisticated Threats: Insider threats, advanced persistent threats (APTs), and phishing attacks.
Zero Trust: A Paradigm Shift
Zero Trust Architecture replaces implicit trust with continuous verification. Its core principle is “never trust, always verify,” meaning no user or device is trusted by default, regardless of whether they are inside or outside the network.
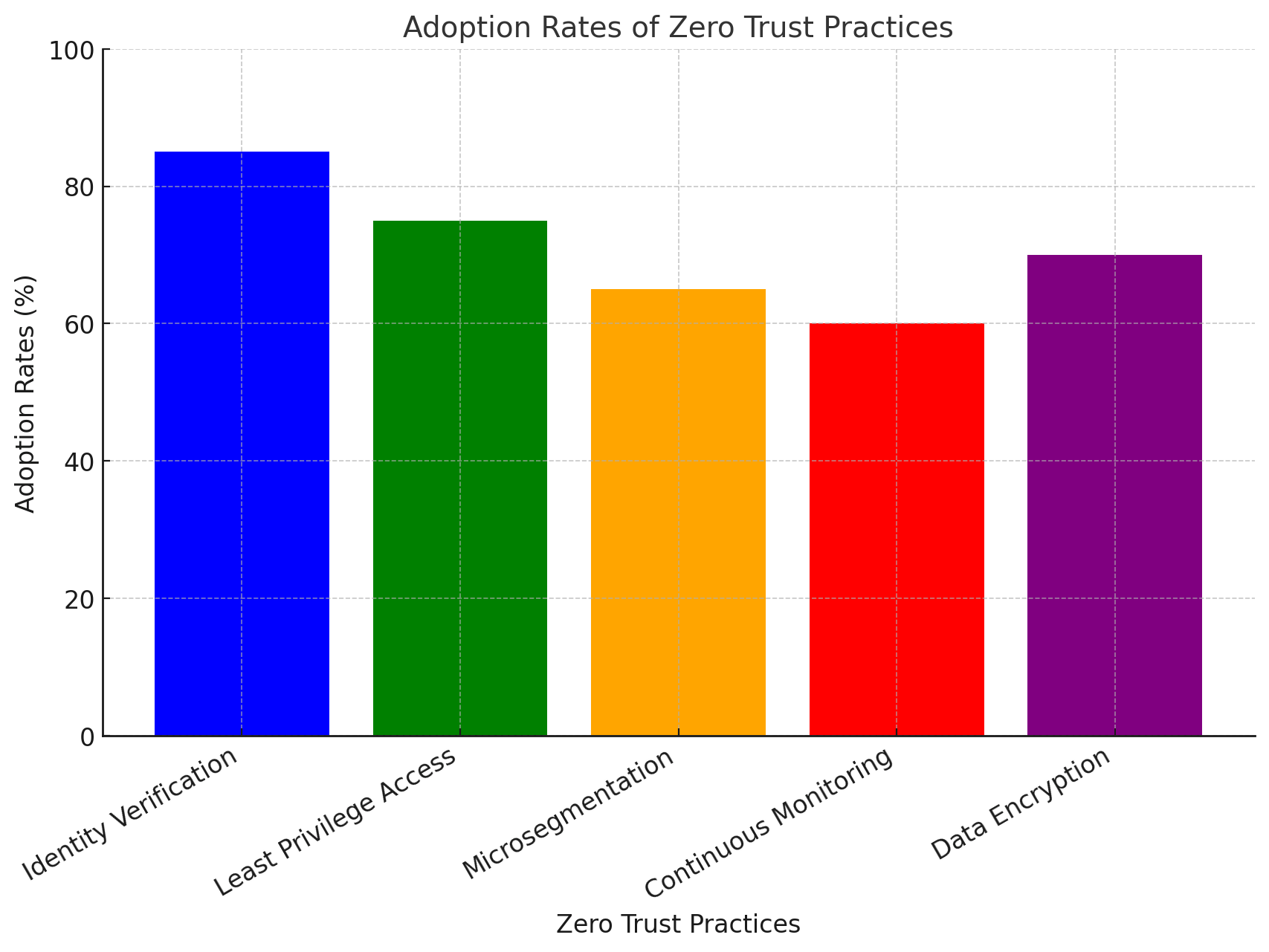
Key Components of Zero Trust
- Identity Verification: Multi-factor authentication (MFA) and identity management.
- Least Privilege Access: Users and devices receive only the access they need.
- Micro-Segmentation: Breaking networks into smaller, isolated zones.
- Continuous Monitoring: Real-time analysis of user behavior and device activity.
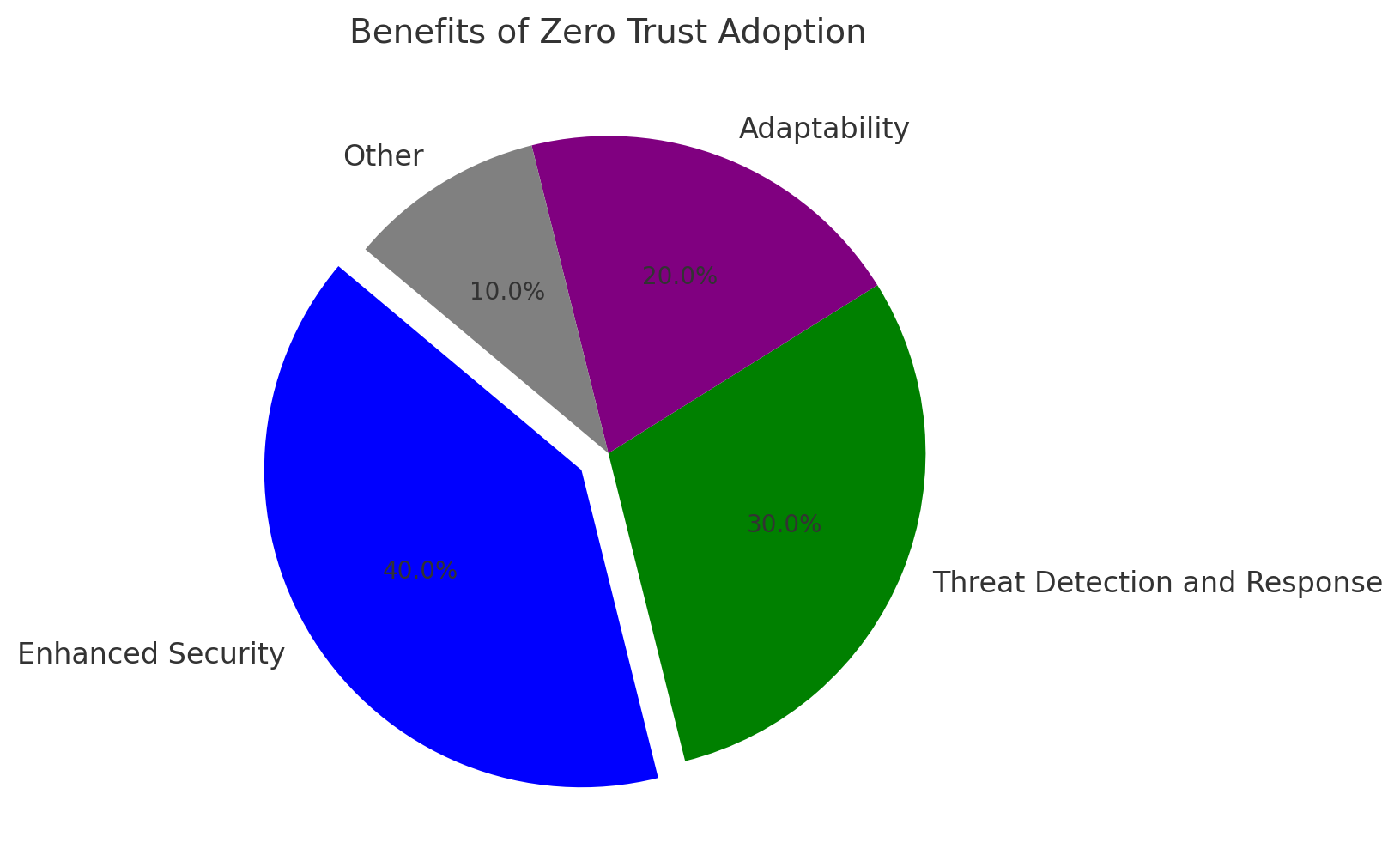
Benefits of Zero Trust Architecture
1. Enhanced Security
Zero Trust minimizes the risk of breaches by eliminating implicit trust and enforcing rigorous access controls.
2. Improved Threat Detection and Response
With real-time monitoring and analytics, organizations can identify anomalies and respond to threats faster.
3. Adaptability to Modern Work Environments
ZTA seamlessly supports remote work, cloud services, and IoT devices, ensuring security without hindering productivity.
Implementing Zero Trust: Key Steps
1. Assess the Current Environment
Identify sensitive assets, user roles, and potential vulnerabilities.
2. Adopt Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Implement MFA, single sign-on (SSO), and role-based access controls.
3. Leverage Network Segmentation
Use micro-segmentation to isolate critical systems and limit lateral movement.
4. Deploy Advanced Threat Detection
Utilize AI and machine learning for continuous monitoring and behavioral analytics
Challenges in Zero Trust Implementation
1. Complexity and Costs
Implementing ZTA requires significant investment in technology, training, and resources.
2. Integration with Legacy Systems
Many organizations struggle to integrate Zero Trust with outdated infrastructure.
3. Cultural Resistance
Employees and stakeholders may resist changes that disrupt workflows or require additional verification steps.
Real-World Use Cases of Zero Trust
1. Remote Workforce Security
Companies like Microsoft and Google have adopted ZTA to secure remote access for thousands of employees.
2. Healthcare Data Protection
Hospitals use Zero Trust to safeguard patient data and ensure HIPAA compliance.
3. Financial Sector Resilience
Banks leverage ZTA to prevent fraud and protect sensitive customer information.
Future Trends in Zero Trust
1. AI-Driven Zero Trust
AI will enhance real-time threat detection and adaptive access controls.
2. Integration with Quantum-Resistant Encryption
As quantum computing advances, ZTA will incorporate encryption techniques to protect against quantum threats.
3. Unified Security Platforms
Future solutions will offer centralized Zero Trust management, combining identity, access, and monitoring into a single platform.
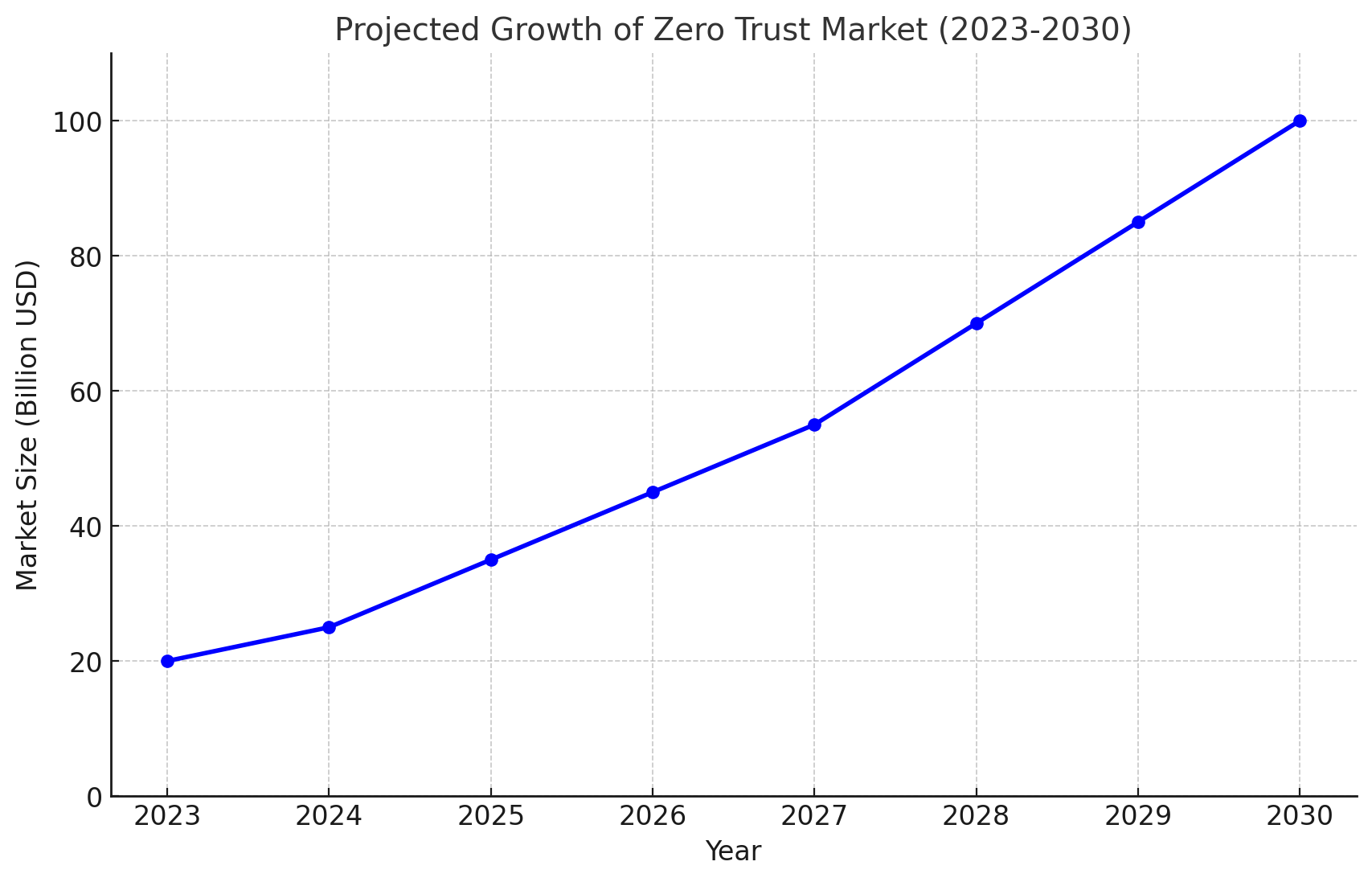
Conclusion
Zero Trust Architecture represents a transformative approach to cybersecurity, addressing the limitations of traditional models in a borderless digital world. By eliminating implicit trust, enforcing least privilege access, and leveraging continuous monitoring, ZTA offers robust defense against modern threats. However, organizations must carefully navigate the challenges of implementation, balancing security with usability.
As cyber threats continue to evolve, adopting Zero Trust is no longer optional but imperative. Whether you're an enterprise leader or a cybersecurity professional, understanding and implementing Zero Trust principles is essential to securing the future of your organization in a borderless world.





