The digital landscape is evolving at an unprecedented pace, and with it, the sophistication of cyber threats continues to escalate. From ransomware attacks targeting critical infrastructure to phishing scams that exploit human vulnerabilities, the stakes have never been higher. Enter artificial intelligence (AI), a game-changing technology that is revolutionizing the field of cybersecurity. By enabling rapid threat detection, real-time response, and predictive analytics, AI is becoming the cornerstone of modern cybersecurity strategies. In this blog post, we explore the rise of AI-driven cybersecurity, how it is shaping threat detection, and why it represents the future of digital defense.
The Growing Cybersecurity Threat Landscape
Before diving into AI’s transformative role, it's essential to understand the growing scope of cybersecurity threats. As organizations increasingly digitize their operations, cybercriminals have exploited this shift to launch more targeted and damaging attacks.
Key Cybersecurity Statistics (2024)
- Global Cybercrime Costs: Expected to reach $10.5 trillion annually by 2025.
- Average Cost of a Data Breach: $4.45 million per incident
- Ransomware Attacks: A new ransomware attack occurs every 11 seconds.
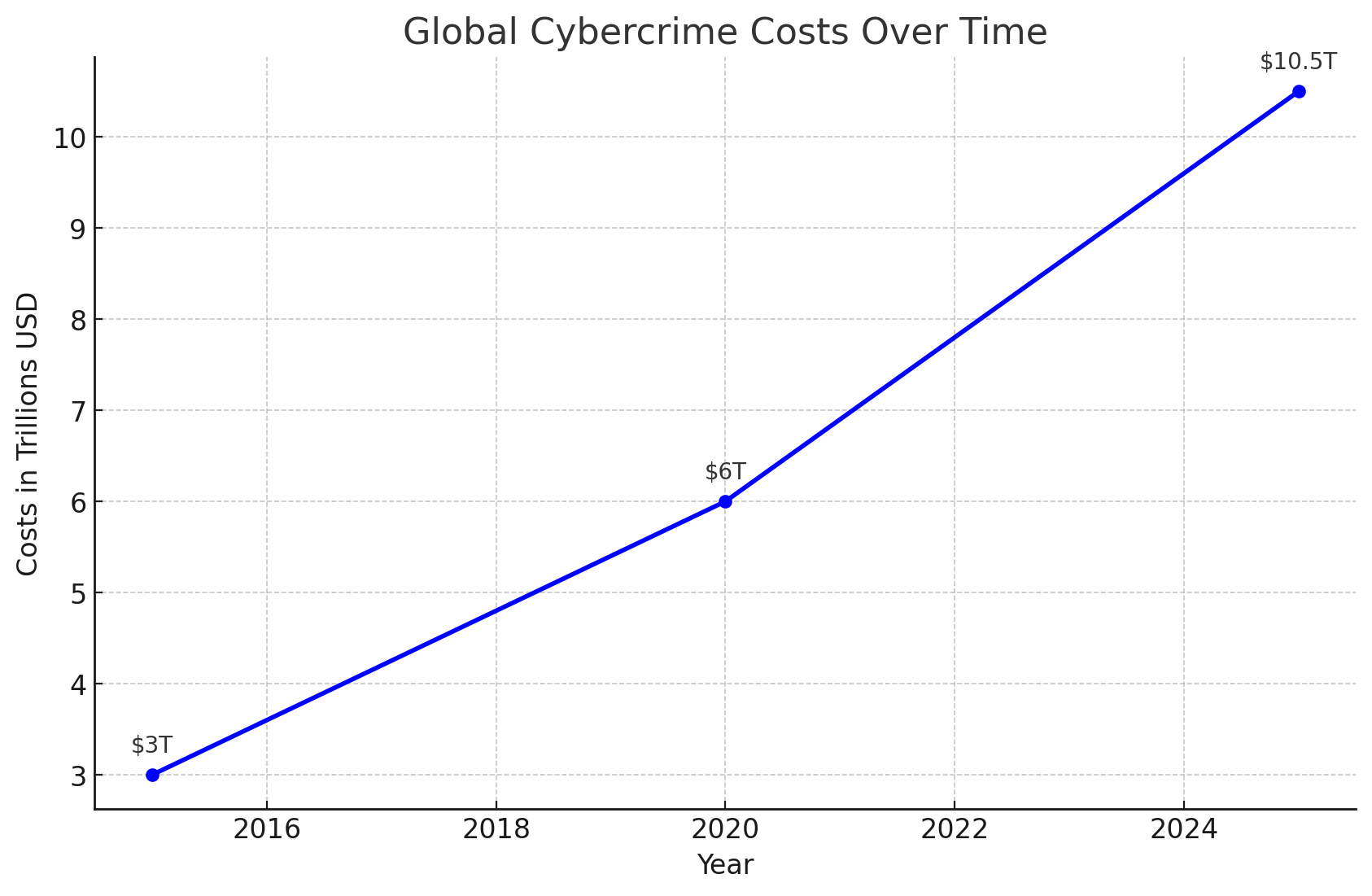
The rising cost of cybercrime underscores the urgent need for advanced solutions. Traditional methods, such as rule-based systems and manual monitoring, are no longer sufficient to keep up with the speed and complexity of modern threats. This is where AI comes into play.
How AI is Transforming Cybersecurity
1. Real-Time Threat Detection
AI excels at analyzing vast amounts of data at lightning speed, making it invaluable for detecting anomalies that might indicate a cyber threat. Machine learning (ML) algorithms can:
- Identify Unusual Patterns: AI can detect deviations in network traffic that might signal a breach.
- Spot Zero-Day Attacks: By identifying patterns and anomalies, AI can flag unknown threats before they are fully understood by human analysts.
- Case Study: AI vs. Zero-Day Threats.
In 2023, a financial institution leveraged AI-powered threat detection tools to identify and neutralize a zero-day exploit within hours of its occurrence, preventing potential losses of over $2 million.
2. Predictive Analytics
AI enables organizations to stay ahead of cybercriminals by predicting potential attack vectors and vulnerabilities. Predictive analytics works by:
- Analyzing Historical Data: AI examines past incidents to forecast future threats.
- Simulating Attack Scenarios: Tools like adversarial AI simulate potential attacks to identify weaknesses.
3. Automation of Incident Response
AI-driven systems can automate repetitive tasks, freeing up cybersecurity professionals to focus on strategic initiatives. Automated incident response includes:
- Quarantining Infected Systems: AI can isolate compromised devices to prevent the spread of malware.
- Alert Prioritization: By ranking threats based on severity, AI ensures that critical issues are addressed first.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
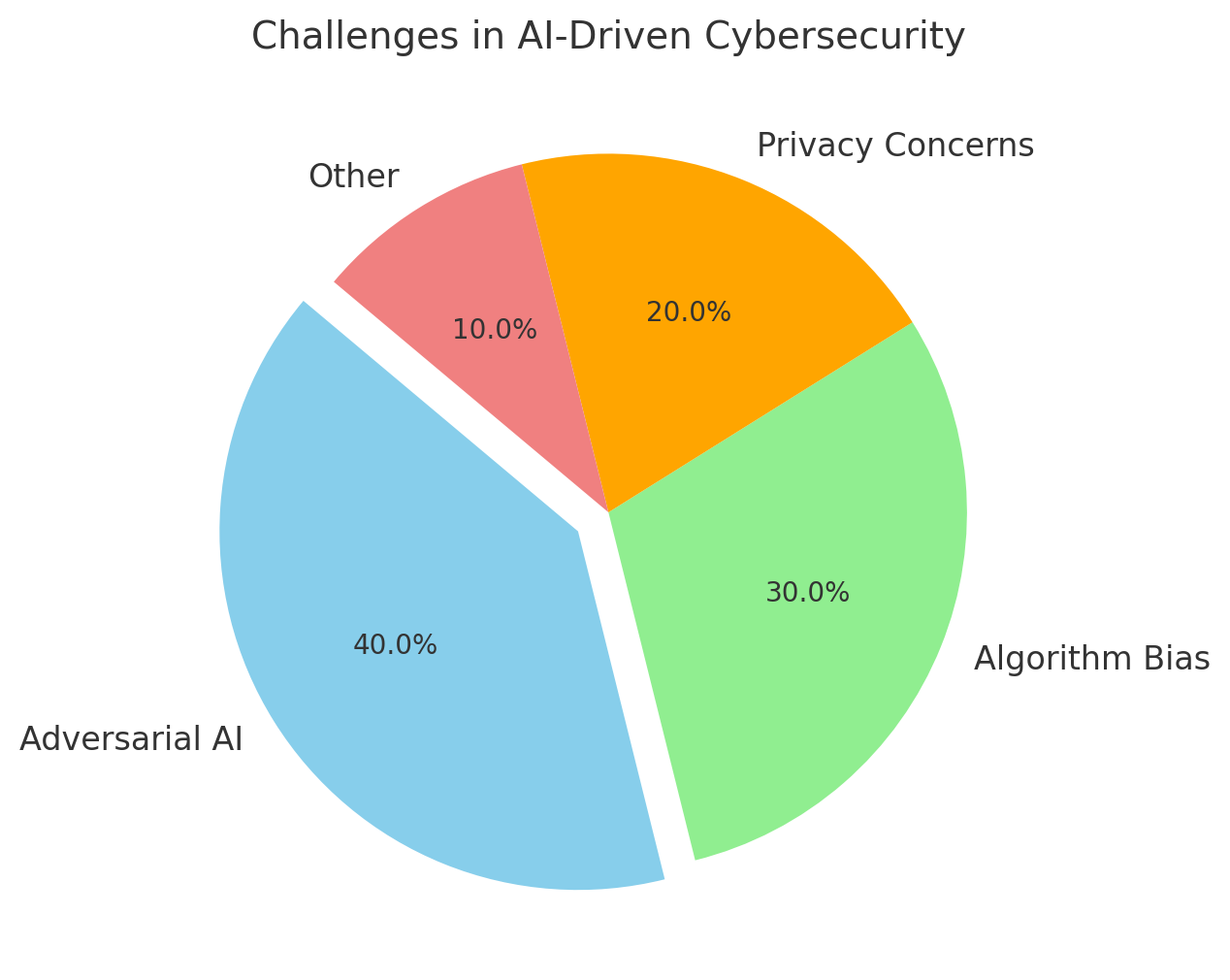
While AI offers immense potential, it is not without challenges:
- Adversarial AI: Cybercriminals are also leveraging AI to create more sophisticated attacks, such as deepfake phishing
- Bias in Algorithms: Biased training data can lead to false positives or overlooked threats.
- Data Privacy: Using AI for cybersecurity often involves processing sensitive information, raising privacy concerns.
The Role of Machine Learning and Big Data
Machine Learning in Action
Machine learning models improve over time by continuously learning from new data. Examples include:
- Supervised Learning: Used for spam filtering and malware classification.
- Unsupervised Learning: Helps identify anomalies in network traffic.
- Reinforcement Learning: Enables AI to optimize responses to dynamic threats.
Big Data’s Role
AI-driven cybersecurity thrives on big data. The more data an AI system has, the better it can:
- Detect trends and anomalies.
- Train predictive models.
- Improve overall accuracy.
- Industry Adoption of AI in Cybersecurity.
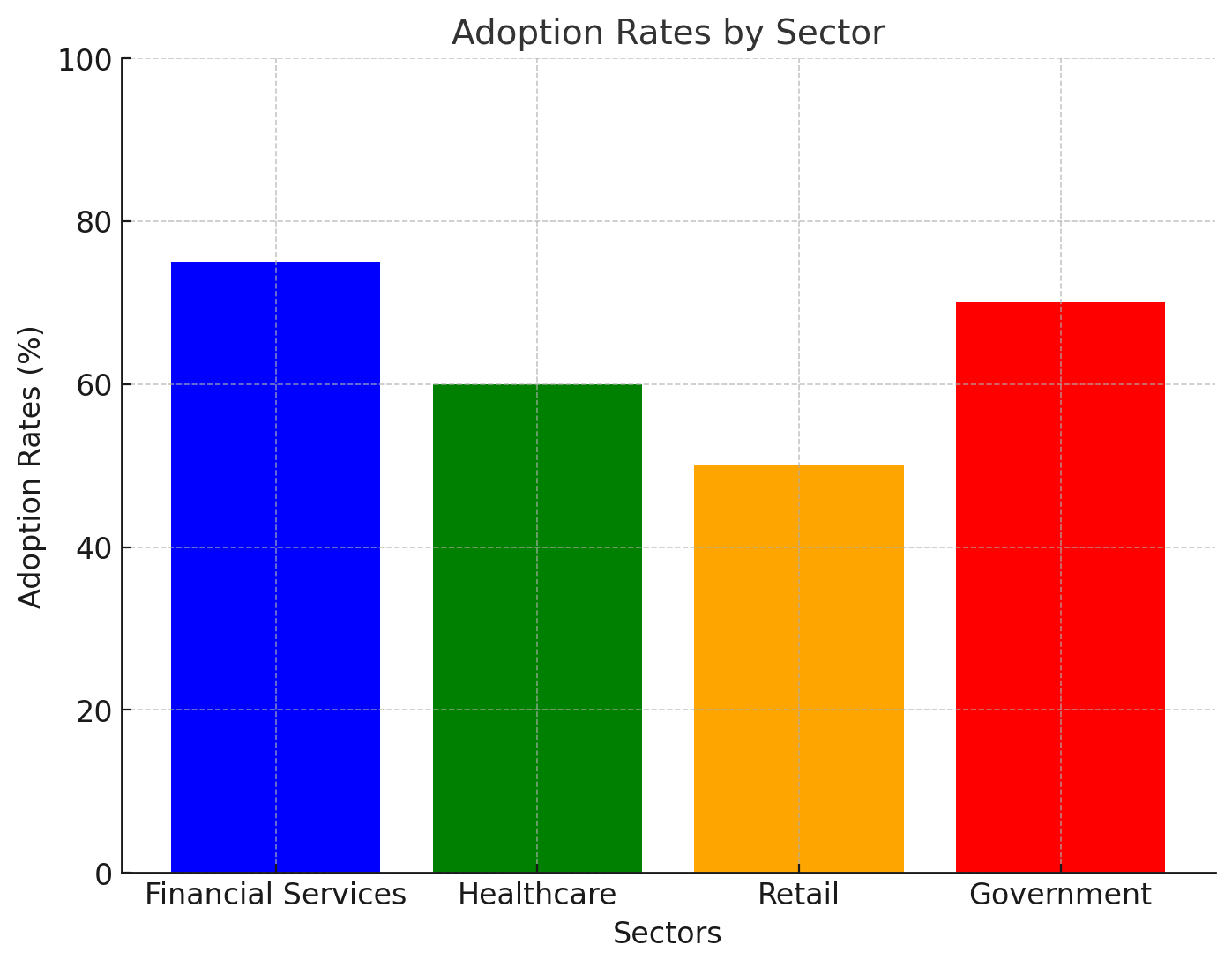
Key Sectors Benefiting from AI
- Healthcare: Protecting patient records and IoT devices.
- Financial Services: Securing transactions and preventing fraud.
- Retail: Safeguarding customer data and point-of-sale systems.
- Government: Enhancing national security and protecting critical infrastructure.
Adoption Rates of AI in Cybersecurity by Sector
Future Trends in AI-Driven Cybersecurity
1. AI-Powered Threat Intelligence
AI will increasingly integrate with threat intelligence platforms to provide actionable insights in real time.
2. Collaborative AI Systems
Future systems will involve collaboration between AI agents and human analysts, creating hybrid models of threat detection.
3. Quantum-Resistant Cryptography
AI will play a key role in developing and deploying encryption techniques that can withstand quantum computing threats.
Conclusion
The rise of AI-driven cybersecurity is not just a trend but a necessity in the face of evolving cyber threats. By enabling real-time detection, predictive analytics, and automated responses, AI is reshaping the way organizations defend against digital adversaries. However, as we embrace this technology, it is crucial to address the challenges it brings to ensure a secure and ethical digital future.
As AI continues to advance, its integration into cybersecurity will only deepen, paving the way for a new era of intelligent and adaptive defense systems. Whether you are an enterprise leader, a cybersecurity professional, or an individual, understanding and leveraging AI-driven cybersecurity will be critical to staying ahead in the digital age.





