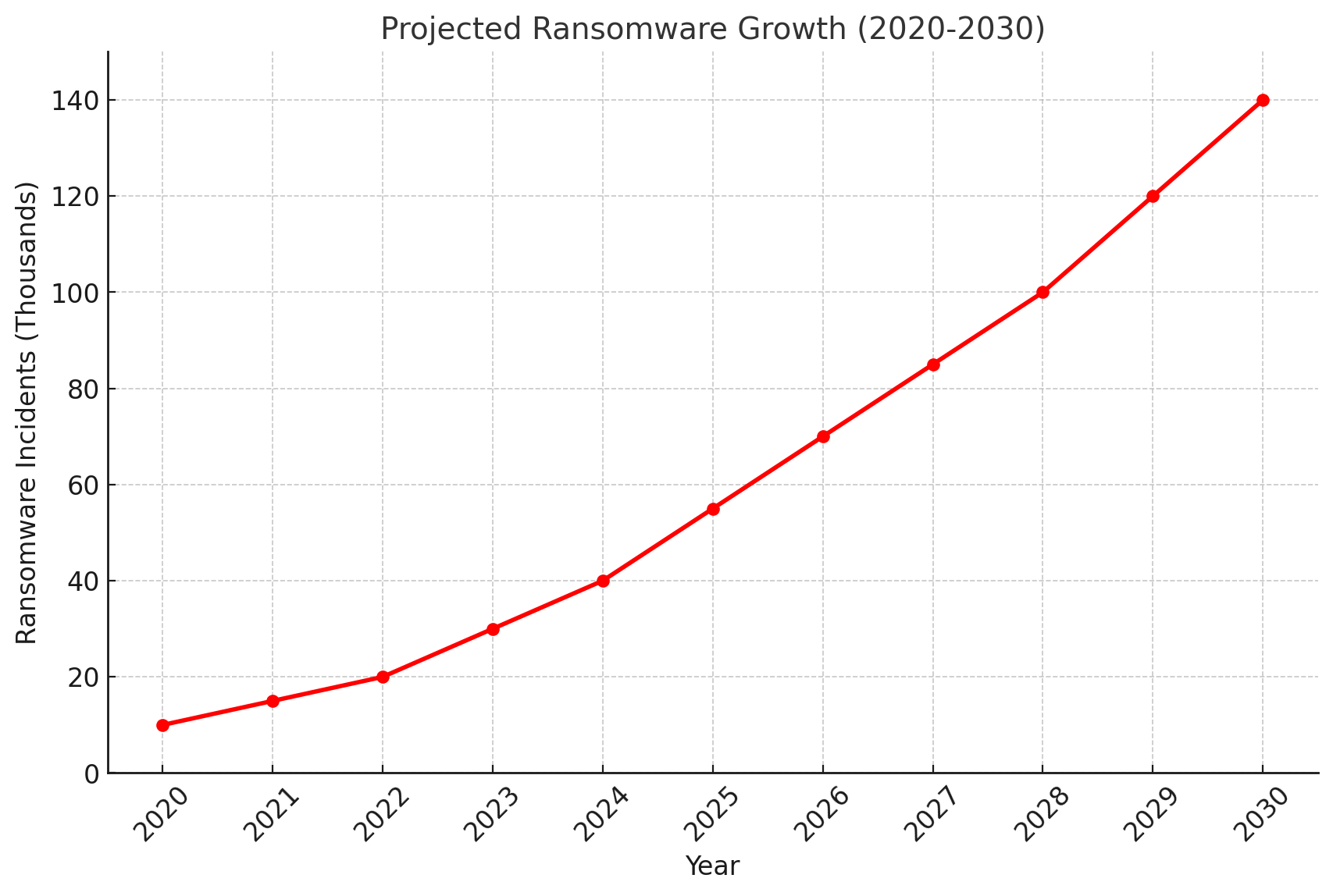
Ransomware attacks have become one of the most significant threats to businesses and individuals in 2025. With cybercriminals leveraging advanced techniques, the stakes are higher than ever before. This blog delves deep into the evolving landscape of ransomware, highlighting trends, implications for developers and businesses, and strategies for mitigation. Using visual aids such as charts, graphs, and infographics, we aim to provide a clear and comprehensive picture of this escalating threat.
Understanding Ransomware
Ransomware is a type of malicious software designed to encrypt data and demand a ransom for its release. While ransomware attacks have been prevalent for over a decade, their sophistication and scale have reached unprecedented levels in recent years
How Ransomware Works
- Infiltration: Attackers use phishing emails, compromised websites, or vulnerabilities in software to breach systems.
- Encryption: Critical files and systems are encrypted, rendering them inaccessible.
- Ransom Demand: A ransom note is delivered, typically demanding payment in cryptocurrency.
- Payment or Recovery: Victims must either pay the ransom or attempt to recover data through backups.
Ransomware in 2025: Key Trends
1. Targeted Attacks on Critical Infrastructure
Cybercriminals are increasingly targeting sectors such as healthcare, energy, and finance, where downtime can have catastrophic consequences.
2. Double and Triple Extortion
Attackers not only encrypt data but also threaten to publish stolen information (double extortion) or target customers and partners (triple extortion).
3. Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS)
RaaS platforms enable even non-technical criminals to deploy sophisticated attacks, increasing the frequency of incidents.
4. Cryptocurrency and Anonymity
Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin continue to facilitate anonymous ransom payments, complicating law enforcement efforts.
Impact on Developers and Businesses
For Developers
- Increased Security Responsibilities: Developers must prioritize secure coding practices to minimize vulnerabilities.
- Threat of Exploited Dependencies: Open-source libraries and dependencies can be a gateway for ransomware.
- Compliance and Standards: Adhering to cybersecurity frameworks such as ISO 27001 and NIST is now essential.
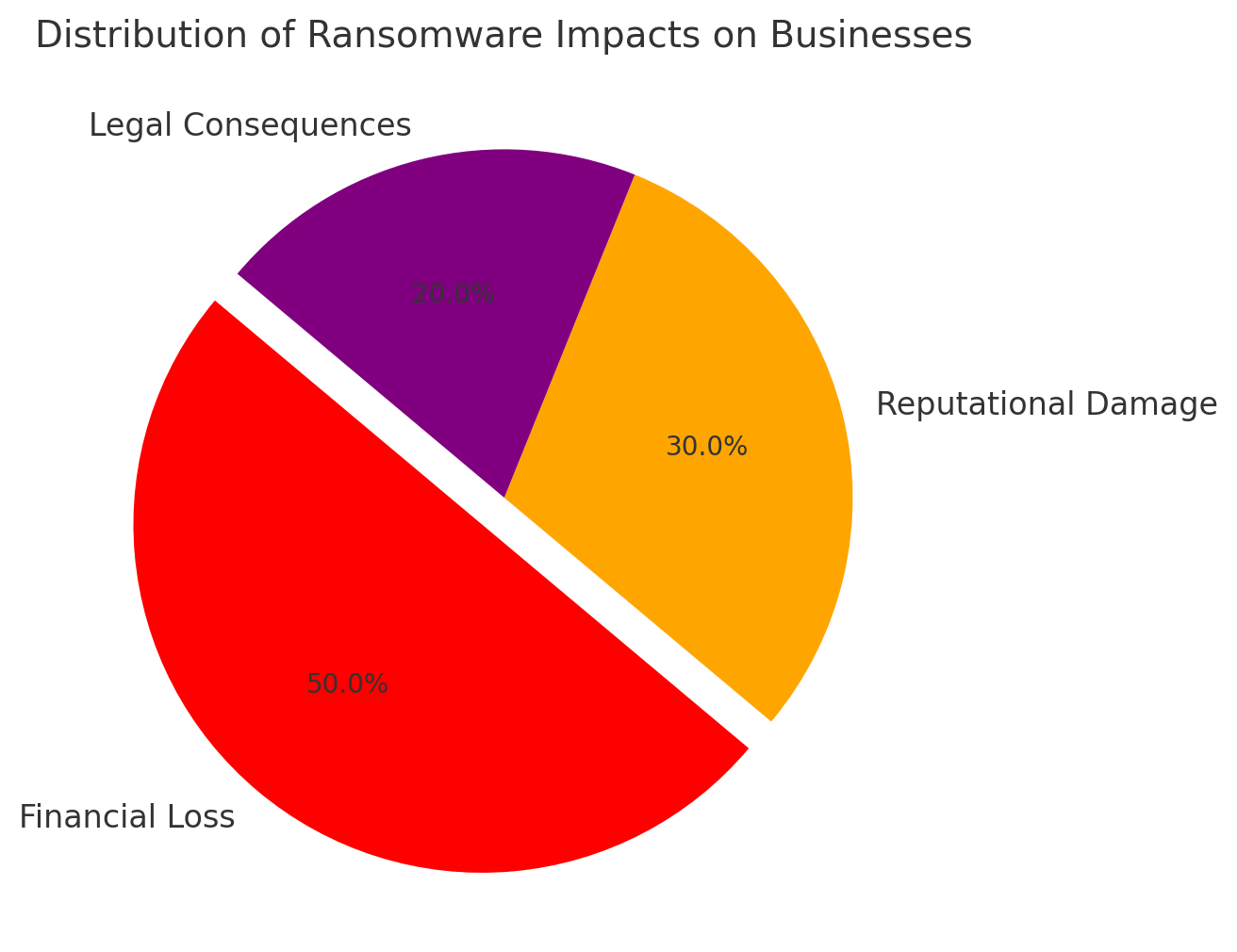
For Businesses
- Financial Losses: The average cost of a ransomware attack has skyrocketed, including ransom payments and downtime.
- Reputational Damage: Publicized breaches erode customer trust and brand credibility.
- Legal and Regulatory Consequences: Non-compliance with data protection laws can result in hefty fines.
Mitigation Strategies
For Developers
- Secure Coding Practices
- Validate user inputs.
- Use updated libraries and frameworks.
- Automated Vulnerability Scanning.
- Incorporate tools like Snyk, OWASP ZAP, or SonarQube into CI/CD pipelines.
- Education and Awareness.
- Stay informed about the latest ransomware tactics.
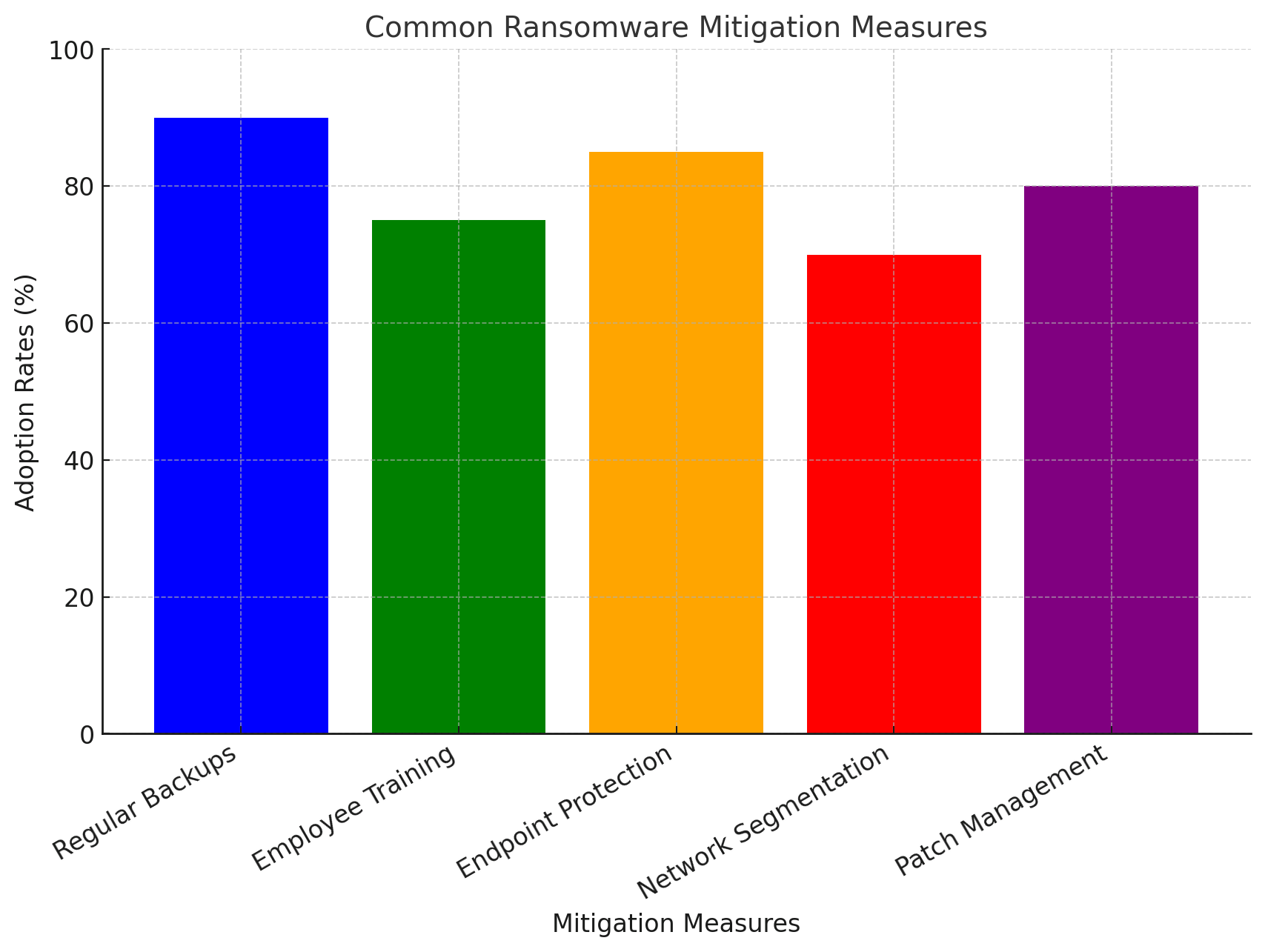
For Businesses
- Regular Backups
- Maintain offline backups and test recovery processes regularly.
- Employee Training.
- Conduct phishing simulations and awareness campaigns.
- Endpoint Protection.
- Deploy endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions.
- Incident Response Plans.
- Develop and rehearse a ransomware-specific response plan.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Fighting Ransomware
1. Threat Detection and Analysis
AI-driven systems analyze patterns to detect ransomware activity before it executes.
2. Behavioral Monitoring
AI monitors user and system behavior for anomalies indicative of ransomware
3. Automated Responses
AI can isolate infected systems, preventing lateral movement.
Case Studies: Ransomware in Action
Case 1: Colonial Pipeline Attack
In 2021, a ransomware attack disrupted fuel supplies across the U.S., highlighting the vulnerability of critical infrastructure
Case 2: Healthcare Under Siege
Hospitals worldwide faced ransomware attacks during the COVID-19 pandemic, risking patient safety.
Case 3: SMBs as Easy Targets
Small and medium-sized businesses often lack robust defenses, making them attractive targets for cybercriminals.
Case Studies: Ransomware in Action
Case 1: Colonial Pipeline Attack
In 2021, a ransomware attack disrupted fuel supplies across the U.S., highlighting the vulnerability of critical infrastructure
Case 2: Healthcare Under Siege
Hospitals worldwide faced ransomware attacks during the COVID-19 pandemic, risking patient safety.
Case 3: SMBs as Easy Targets
Small and medium-sized businesses often lack robust defenses, making them attractive targets for cybercriminals.
Future Outlook
1. Government Regulations
Governments are enacting stricter regulations to combat ransomware, including mandatory reporting of attacks.
2. Collaboration Across Sectors
Public-private partnerships aim to enhance collective defense mechanisms.
3. Emerging Technologies
Quantum computing and advanced cryptography hold promise for thwarting ransomware attacks.
Conclusion
Ransomware is an ever-growing menace, demanding vigilance from developers, businesses, and governments alike. By adopting proactive measures, investing in advanced technologies, and fostering collaboration, we can mitigate the threat and protect our digital future.
As we navigate the complex cybersecurity landscape of 2025, one thing is clear: staying ahead of ransomware requires constant innovation and a commitment to resilience. What steps is your organization taking to combat ransomware? Share your insights in the comments below!





