Blockchain technology, originally designed to support cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, has evolved far beyond its initial use case. Today, enterprises across industries are leveraging blockchain's decentralized, secure, and transparent nature to solve a wide variety of challenges. From improving supply chain management to ensuring data security, blockchain is rapidly becoming a cornerstone in the development of innovative IT solutions.
In this blog, we explore the top enterprise use cases of blockchain technology in IT development, showcasing its transformative potential in various sectors. We’ll dive into examples, real-world applications, and case studies, providing a comprehensive look at how businesses can harness the power of blockchain.
What is Blockchain?
Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology that enables secure, transparent, and tamper-proof record-keeping. In a blockchain, data is stored in blocks that are linked together in a chain, with each block containing information such as transaction records, timestamps, and cryptographic hashes. Once information is added to the blockchain, it is virtually immutable, making it an ideal solution for industries that require high levels of transparency and security.
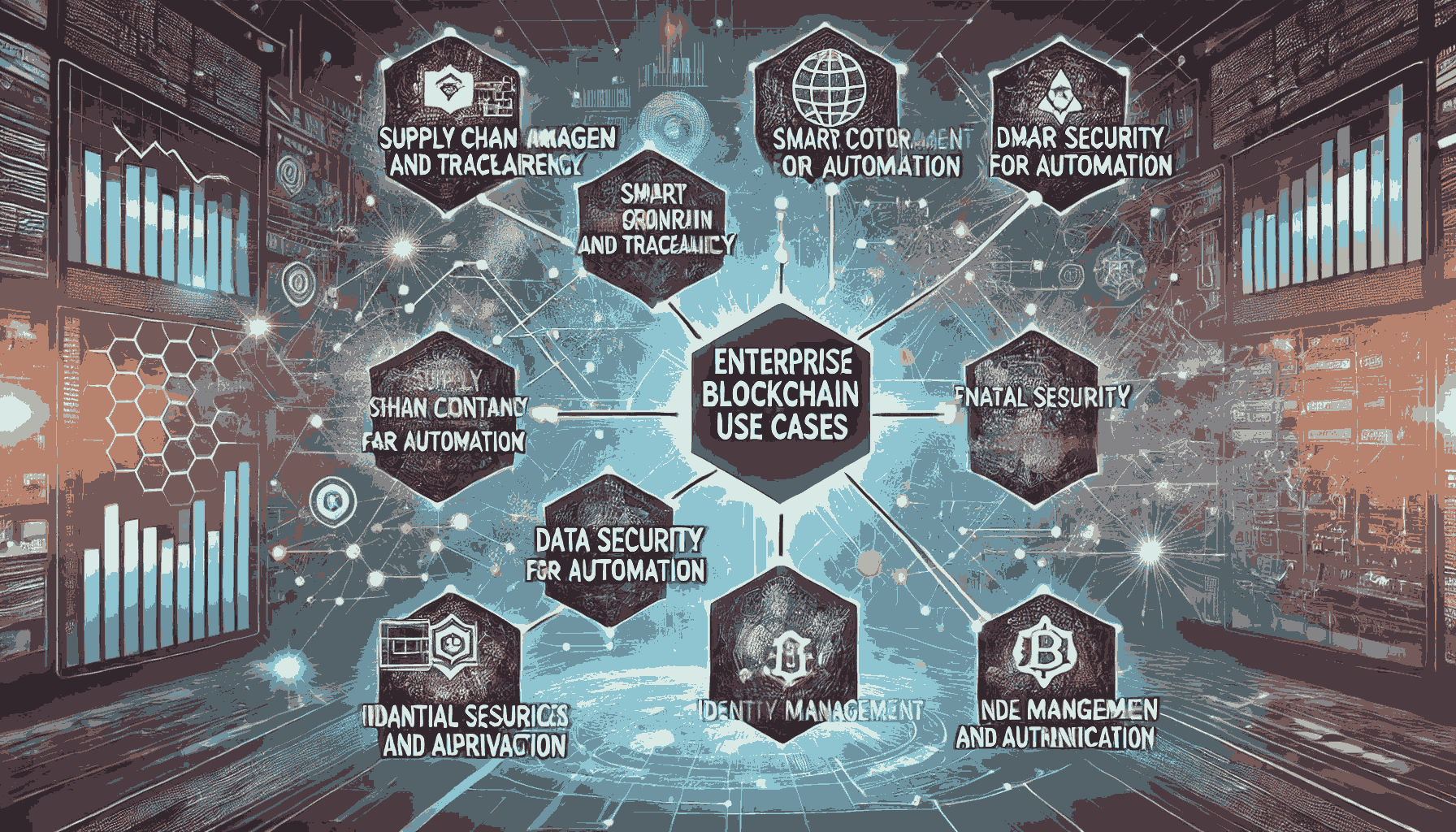
Top Enterprise Use Cases for Blockchain in IT Development
1. Supply Chain Management and Traceability
Supply chain management has long been a challenge for many industries, with issues such as counterfeit goods, inefficiencies, and lack of transparency. Blockchain can revolutionize supply chain processes by providing end-to-end visibility, ensuring that every transaction is recorded and traceable in real-time.
Example:
A major food retailer implemented blockchain technology to track the journey of its products from farm to store. Using a blockchain-powered system, the retailer was able to trace every step of the food’s supply chain, ensuring product authenticity and food safety. Consumers could scan QR codes on packaging to access detailed information about the food’s origins and journey.
Benefit: Enhanced transparency, improved food safety, reduced counterfeiting, and increased consumer trust.
2. Smart Contracts for Automation
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. Blockchain-based smart contracts automate processes, reducing the need for intermediaries, and ensuring that contractual obligations are fulfilled automatically when predefined conditions are met.
Example:
A real estate company uses smart contracts to facilitate property transactions. Once all conditions of the sale are met (e.g., buyer’s payment, seller’s documents), the smart contract automatically transfers ownership of the property and disburses funds to the seller. This eliminates the need for lawyers, notaries, and escrow agents.
Benefit: Reduces operational costs, improves efficiency, and mitigates the risk of fraud.
3. Data Security and Privacy
In the digital age, data breaches are becoming more frequent, and companies are under constant pressure to protect sensitive information. Blockchain’s decentralized nature and cryptographic security features make it an ideal solution for enhancing data security and protecting privacy.
Example:
A healthcare provider leverages blockchain to store patient records. Each patient's data is encrypted and stored in a decentralized manner, with only authorized parties having access to the data. Blockchain ensures that the records cannot be tampered with, offering a secure and transparent way to manage sensitive health information.
Benefit: Enhanced security, privacy protection, and reduced risks of data breaches.
4. Financial Services and Cross-Border Payments
Blockchain has the potential to disrupt the financial services industry by streamlining cross-border payments, reducing transaction fees, and improving overall transaction speed. By eliminating intermediaries, blockchain makes it possible to send money directly from one party to another.
Example:
A global bank uses blockchain to facilitate cross-border payments. Previously, international money transfers could take days to process and involved several intermediaries. With blockchain, payments are completed in real-time, with reduced fees and improved transparency.
Benefit: Faster payments, reduced fees, enhanced transparency, and global scalability.
5. Identity Management and Authentication
Managing digital identities securely is a growing concern for businesses, especially as the number of online transactions and interactions increases. Blockchain can help organizations create decentralized, tamper-proof digital identity systems, allowing individuals to control their own personal data and grant permissions to access it.
Example:
A government agency uses blockchain to manage citizens' digital identities. Each citizen has a blockchain-based digital ID that is secure and verifiable. This system allows citizens to access services like voting, healthcare, and tax filing using a single, secure identity.
Benefit: Increased security, privacy, and control over personal information.
Blockchain Use Case in Action: Case Study of IBM and Maersk
- Company: IBM and Maersk
- Industry: Shipping and Logistics
Challenge:
The global shipping industry faces significant challenges in tracking shipments, verifying authenticity, and handling paperwork. Traditional processes are paper-based, time-consuming, and prone to errors, leading to inefficiencies and delays.
Solution:
IBM and Maersk collaborated to create TradeLens, a blockchain-powered shipping solution. This platform allows all participants in the supply chain, including shipping companies, ports, customs authorities, and freight forwarders, to share real-time data securely. Every shipment’s journey is tracked on the blockchain, providing transparency and security at every step.
Outcome:
- Reduced paperwork and manual processes, saving time and resources.
- Improved transparency, reducing fraud and errors.
- Enhanced collaboration between stakeholders, improving supply chain efficiency.
- Faster processing of shipments and lower operational costs.
Conclusion:
TradeLens demonstrates how blockchain can solve long-standing challenges in logistics by providing a transparent and secure platform for all parties to collaborate. By utilizing blockchain, Maersk and IBM have revolutionized the shipping industry, setting a new standard for efficiency and security.
Conclusion: Blockchain's Transformative Potential in IT Development
Blockchain technology is no longer limited to the realm of cryptocurrency. Its decentralized and secure nature makes it a valuable tool for solving complex business challenges across industries. Whether it’s improving supply chain transparency, automating contracts with smart contracts, enhancing data security, or transforming financial services, blockchain is quickly becoming a critical component of IT development strategies.
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing IT development by offering secure, transparent, and decentralized solutions. Its ability to enhance data security, streamline operations, and reduce fraud makes it a game-changer for IT companies. By eliminating intermediaries, blockchain enables cost-effective transactions and secure smart contracts. IT firms leverage blockchain for cybersecurity, cloud storage, and supply chain management, ensuring data integrity and seamless automation. As industries embrace decentralized applications (DApps), blockchain fosters innovation in fintech, healthcare, and logistics. With its potential to redefine data management and enhance trust, blockchain is shaping the future of IT, driving efficiency and scalability in digital solutions.
As we move into 2025 and beyond, blockchain’s applications will continue to evolve, providing even greater opportunities for innovation and efficiency. Companies that embrace blockchain will be well-positioned to stay ahead of the curve and meet the demands of an increasingly digital world.
FAQs
Blockchain enhances data security by decentralizing data storage and utilizing cryptographic techniques to ensure that data cannot be tampered with or altered without detection. Once a piece of data is recorded on the blockchain, it is linked to previous data and cannot be changed, offering a high level of security and integrity.
Yes, blockchain has numerous applications beyond cryptocurrency. It is being used in industries such as supply chain management, healthcare, finance, identity management, and more. Its ability to provide secure, transparent, and tamper-proof record-keeping makes it valuable in various business sectors.
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. They automatically enforce and execute contract terms once predefined conditions are met, eliminating the need for intermediaries and reducing the risk of errors or fraud.
Small businesses can benefit from blockchain by using it for secure payment processing, inventory management, and improving customer trust through transparent supply chains. Blockchain can also reduce transaction fees and improve the efficiency of cross-border payments, making it a cost-effective solution for small businesses.





