Introduction
Have you ever wondered how changes in retail inflation can impact your daily life and the overall economy? Recently, retail inflation in India has dropped to its lowest point in six years, sparking interest and discussions about what this means for consumers and businesses alike. As inflation rates affect everything from the cost of goods to purchasing power, understanding this shift is essential for making informed decisions in both personal and business finance.
True Value Infosoft, the top app development company in India, recognizes that economic trends like these play a crucial role in shaping the future of businesses. With inflation at a six-year low, companies must adapt to new consumer behaviors, optimize their operations, and leverage technology to stay ahead.
Understanding Retail Inflation
Retail inflation refers to the rate at which the prices of goods and services in the retail market increase over time. This is measured by the Consumer Price Index (CPI), which tracks the average change in prices paid by urban consumers for a representative basket of goods and services. When inflation is high, consumers find that their money doesn't go as far as it once did, affecting their purchasing power.
Factors Affecting Retail Inflation:
- Supply and Demand Dynamics: If demand for a product exceeds supply, the prices rise. Similarly, when supply outpaces demand, prices tend to fall.
- Government Policies: Fiscal and monetary policies such as taxation and interest rates can either stimulate or suppress inflation.
- Global Events: Natural disasters, pandemics, and geopolitical tensions can disrupt supply chains, affecting the prices of essential goods.
Key Drivers Behind the Six-Year Low in Retail Inflation
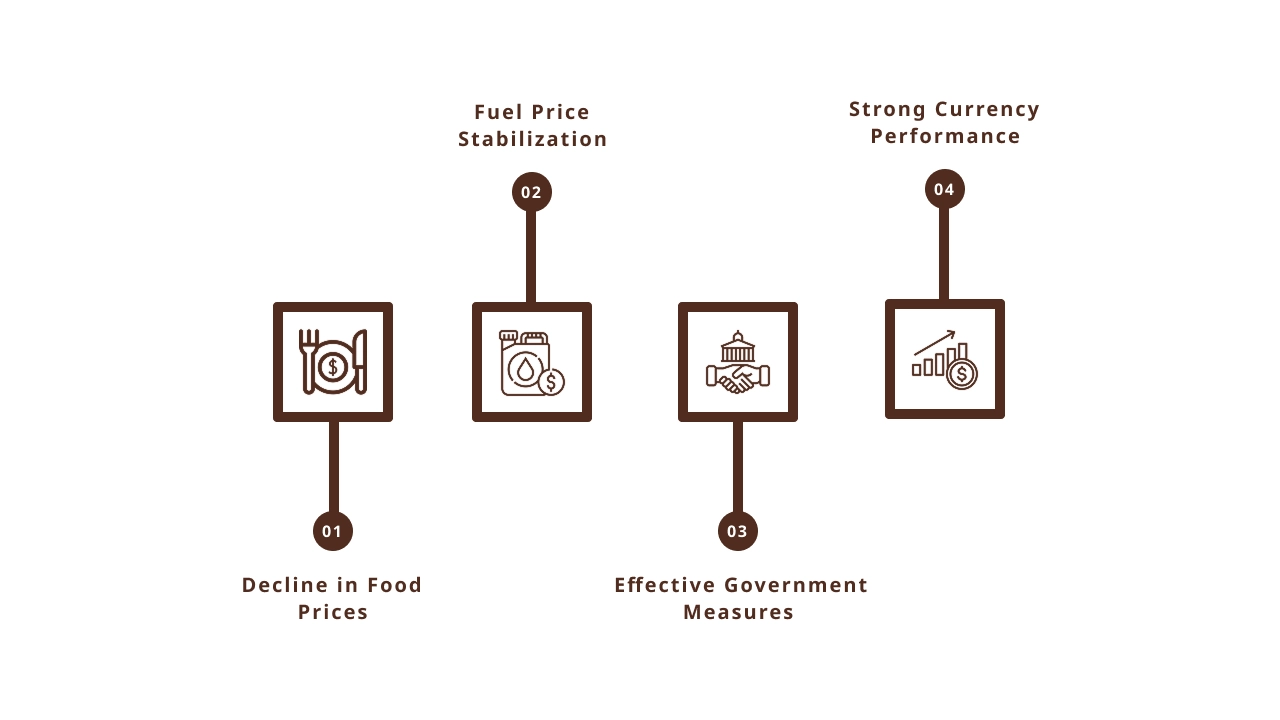
Several key factors have contributed to retail inflation hitting a six-year low in India:
1. Decline in Food Prices
One of the primary reasons behind the decrease in retail inflation is the drop in food prices. The government has taken several measures to ensure a stable supply of food grains and other essential items. Additionally, favorable monsoons and improved agricultural productivity have contributed to lower food prices.
- Impact on Consumers: Consumers are now paying less for everyday essentials like vegetables, fruits, and pulses. This is especially beneficial for households with lower income brackets that spend a significant portion of their earnings on food.
2. Fuel Price Stabilization
Fuel prices, particularly petrol and diesel, have been relatively stable, even decreasing at certain points. With lower global crude oil prices, the Indian government has been able to keep domestic fuel prices under control, reducing the pressure on inflation.
- Impact on Transport and Logistics: Lower fuel prices translate into lower transportation and logistics costs, which, in turn, reduce the prices of goods across the economy.
3. Effective Government Measures
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has been proactive in keeping inflation under control through its monetary policies. Its consistent interest rate adjustments have helped curb excessive inflationary pressure. The government’s efforts in improving supply chains and reducing bottlenecks have also played a significant role.
- Impact on Investment: Stable inflation rates promote business investment by reducing uncertainty, leading to growth in various sectors such as manufacturing and services.
4. Strong Currency Performance
A strong Indian rupee, in comparison to other major currencies, has helped reduce the cost of imports. As India imports a significant amount of goods, especially oil and machinery, a strong rupee helps in curbing inflationary pressures on imported goods.
- Impact on Imported Goods: Consumers have seen lower prices for imported goods, further contributing to the decline in overall inflation.
Broader Economic Implications of Low Retail Inflation
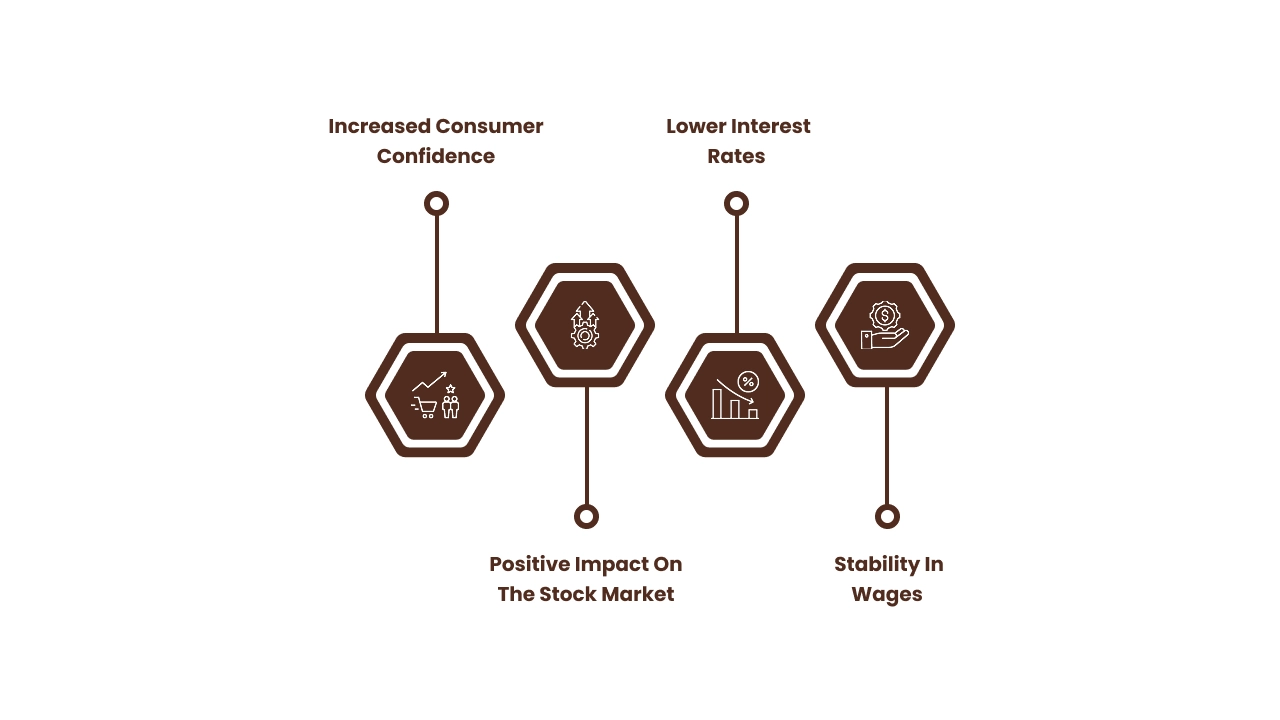
1. Increased Consumer Confidence
When retail inflation remains low, consumers feel more confident in their financial stability. With stable prices, they are less likely to worry about price hikes, leading to increased spending in the economy.
- Impact on Consumer Behavior: This translates into more purchases, both essential and discretionary, boosting the retail and services sectors.
2. Positive Impact on the Stock Market
Lower inflation typically leads to a more favorable environment for businesses. With lower costs, companies can maintain or increase profit margins. This stability can increase investor confidence, often reflected in higher stock market valuations.
- Impact on Investors: The low inflationary environment has led to greater interest in equities, benefiting both institutional and retail investors.
3. Lower Interest Rates
One of the most immediate effects of low inflation is the reduction in interest rates by the central bank. With lower interest rates, borrowing becomes cheaper for businesses and consumers alike, stimulating economic growth.
- Impact on Borrowers: Lower loan and mortgage rates lead to higher consumer spending, home purchases, and business expansion.
4. Stability in Wages
Low inflation means that wages are more likely to keep up with the cost of living. As the purchasing power of consumers remains stable, employees are less likely to demand higher wages to compensate for rising prices.
- Impact on Workers: Workers can expect steady income without the fear of inflation eroding their real wage value.
True Value Infosoft's Role in the Evolving Economic Landscape
As businesses face a dynamic economic environment, True Value Infosoft, the top app development company in India, continues to lead the way in delivering cutting-edge solutions. Our expertise in building apps that optimize supply chain management, e-commerce platforms, and financial services can help businesses leverage the current economic conditions to their advantage.
Whether it's through improving customer engagement with mobile apps or streamlining operations with enterprise solutions, True Value Infosoft is committed to helping businesses thrive in a low-inflation environment.
Potential Risks and Challenges of Low Inflation
While low inflation may seem beneficial at first glance, it does come with its own set of challenges:
1. Risk of Deflation
While low inflation is generally a positive sign, it can lead to deflation in extreme cases. Deflation can reduce consumer spending, as people wait for prices to fall further. This creates a vicious cycle of decreased demand and economic contraction.
- Impact on Businesses: Businesses may struggle with reduced sales and profitability, leading to layoffs and cost-cutting measures.
2. Lower Economic Growth
A prolonged period of low inflation might also signal weak demand for goods and services. This could be indicative of an economy struggling to grow, as businesses face difficulties in raising prices or generating higher revenues.
- Impact on Employment: Lower economic growth can lead to higher unemployment rates, especially in sectors reliant on consumer spending.
3. Impact on Debt
For borrowers, low inflation can mean that the real value of their debt remains unchanged. This may seem like an advantage, but it can also discourage borrowing and investment in the economy.
- Impact on Government Spending: The government might struggle with financing projects as tax revenue may not grow as quickly as expected due to low inflation.
What the Future Holds: A Stable Economy or Potential Challenges?
The low retail inflation rate presents a picture of economic stability, but the future remains uncertain. Global factors like trade tensions, climate change, and technological advancements can affect inflation trends. The key to maintaining stability lies in effective monetary and fiscal policies that keep inflation manageable without stifling growth.
Conclusion
The current retail inflation rate hitting a six-year low is a testament to India's economic resilience. By understanding the various drivers and implications of this trend, consumers, businesses, and policymakers can make informed decisions. It presents an opportunity for the economy to grow steadily while ensuring that inflationary pressures do not hinder progress.
True Value Infosoft remains committed to providing innovative solutions that enable businesses to navigate through changing economic conditions, ensuring growth and stability in times of uncertainty.
FAQs
Retail inflation is the rate at which the prices of goods and services in the retail market rise over a specific period, typically measured by the Consumer Price Index (CPI).
Consumers benefit from lower prices for goods and services, which improves their purchasing power and overall economic well-being.
Factors such as declining food prices, stable fuel prices, effective government policies, and a strong currency have contributed to the low inflation rate in India.
While low inflation is generally good, it can lead to deflation if the rate becomes too low. This could result in reduced consumer spending and economic stagnation.
Businesses can capitalize on low inflation by reducing costs, improving operational efficiency, and enhancing customer experience, which can drive demand and profitability.





